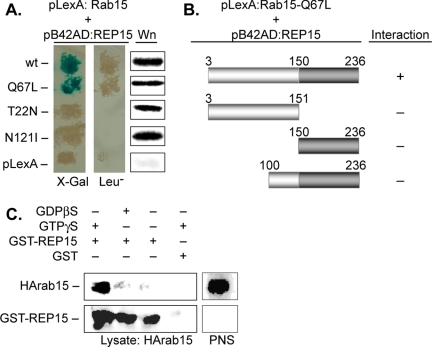
Figure 2.
REP15 binding to Rab15 is guanine nucleotide dependent. (A) Yeast strains expressing REP15 fused to the activation domain of B42 (pB42AD:REP15) were mated with strains expressing wild type (wt) or the indicated mutants of Rab15 fused to LexA (pLexA:Rab15), and the resulting diploids were examined for protein interactions. Blue colonies on 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactoside or growth on Leu-plates indicate specific interactions between REP15 and Rab15. Western analysis (Wn) confirmed comparable levels of Rab15 expression in all diploid strains. (B) The indicated amino- and carboxy-terminal truncations of REP15 were fused to the activation domain of B42, mated with a yeast strain expressing Rab15-Q67L, and the resulting diploids were examined for the presence (+) or absence (-) of protein interactions using a yeast two-hybrid approach as described above. (C) A postnuclear supernatant (PNS) prepared from HeLa cells expressing wild-type HA-tagged Rab15 (HArab15) was incubated in the absence (-) or presence (+) of GTPγS or GDPβS before incubation with GST-REP15. Complexes were isolated and examined by Western analysis using antibodies for HARab15 and GST-REP15.