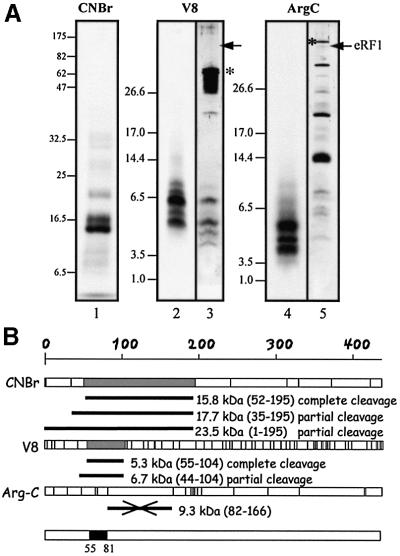
Fig. 6. Mapping the crosslinking site on wild-type eRF1. (A) Determination of the size of the 32P-labeled eRF1p* fragments after specific treatments. In lanes 1, 2 and 4, eRF1p* was treated by CNBr (Met↓X), protease V8 (Glu↓X and Asp↓X) and protease Arg-C (Arg↓X), respectively. Samples were analyzed by either 12.5% Tris–glycine (lane 1) or 16.5 % Tris–tricine (lanes 2–5) SDS–PAGE. Digestion of 15 µg of eRF1 with either V8 (lane 3) or Arg-C (lane 5) proteases followed by visualization by silver staining. Asterisks indicate the positions of V8 and Arg-C on the gel. Arrows indicate the position of full-length eRF1. (B) Schematic representation of the sites of cleavage of full-length human eRF1by CNBr or V8 and Arg-C proteases; sites are represented as vertical bars. The size of 32P-labeled peptides in agreement with the data of (A) are shown in gray (fragments resulting from complete cleavage) or as black bars (incomplete cleavage) for CNBr and V8. The data obtained with Arg-C show that the 9.3 kDa peptide, positions 82–166 (crossed black bar), is not labeled. Compilation of the data is shown as a black box (positions 55–81 of human eRF1).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.