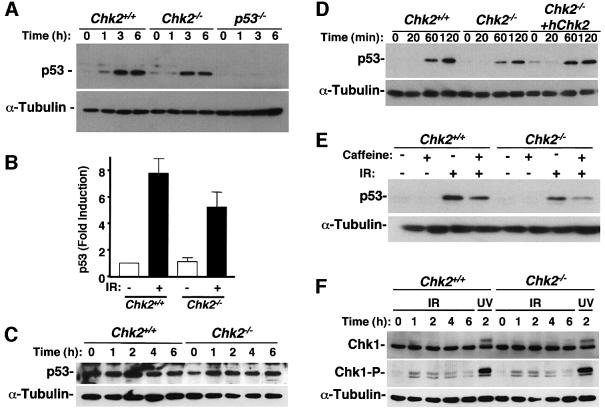
Fig. 5. IR-induced stabilization of p53 in Chk2–/– thymocytes, MEFs and ES cells. (A) Immunoblot analysis of the time course of p53 abundance after exposure of thymocytes from Chk2+/+, Chk2–/– and p53–/– mice to IR (5 Gy). (B) Quantitation of p53 abundance 4 h after exposure of Chk2+/+ or Chk2–/– thymocytes to IR as in (A). Data are expressed as fold induction relative to the amount of p53 in non-irradiated cells and are means ± standard deviation of values from five independent experiments. (C) Protein levels of p53 in MEFs from Chk2+/+ or Chk2–/– mice harvested at the indicated times after 10 Gy IR. (D) Effect of expression of recombinant human Chk2 on the IR-induced stabilization of p53 in Chk2–/– ES cells. (E) Stabilization of p53 protein after IR is dependent on a caffeine-sensitive pathway in Chk2–/– cells. Chk2+/+ and Chk2–/– ES cells were pre-treated with or without 5 mM caffeine for 1 h and cell lysates were made 2 h after IR. (F) Activation of Chk1 in response to IR. Immunoblot analysis of the time course of Chk1 and Ser345-phosphorylated Chk1 in Chk2+/+ or Chk2–/– MEFs after IR (10 Gy) or UV irradiation (50 J/m2).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.