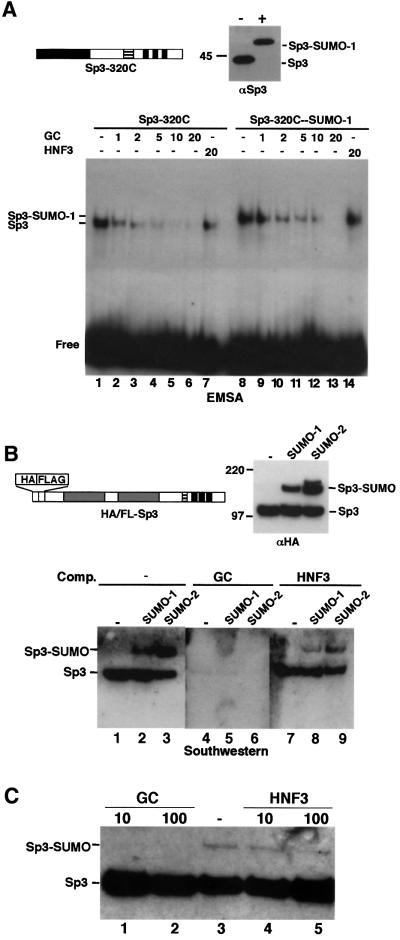
Fig. 7. SUMO-modified Sp3 binds specifically DNA. (A) A C-terminal Sp3 fragment (Sp3-320C) was subjected to in vitro conjugation with SUMO-1 in the absence (–) or presence (+) of enzymes. Subsequently, reactions were analysed by immunoblotting (top right, αSp3) and EMSA. All DNA-binding reactions contained 0.1 ng of 32P-labelled GC oligonucleotide and various amounts (1- to 20-fold molar excess) of unlabelled GC or HNF3 oligonucleotides, as indicated. (B) Purified HA/FLAG-tagged Sp3 was subjected to in vitro conjugation with SUMO-1 or SUMO-2 and analysed by immunoblotting (top right, αHA) and southwestern analysis. For southwestern analysis, SUMOylation reaction products were separated by 8% SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose and subsequently incubated with 32P-labelled GC-box oligonucleotide in the absence (lanes 1– 3) or presence (lanes 4–6) of 100-fold molar excess of a specific competitor (GC box) or an unspecific (HNF3 site) (lanes 7–9) oligonucleotide. (C) Sp3 is not a target for SUMOylation when bound to DNA. Epitope-tagged recombinant Sp3 was subjected to SUMO-1 modification in the absence (lane 3) or presence of 10 and 100 ng of GC-box oligonucleotide (lanes 1 and 2) or HNF3-binding site oligonucleotide (lanes 4 and 5). Reaction products were separated by 8% SDS–PAGE and analysed by immunoblotting with αHA antibodies.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.