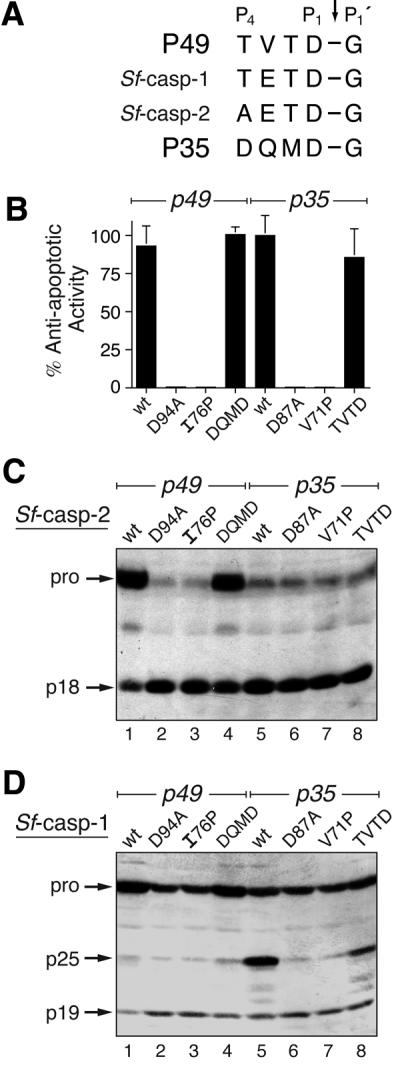
Fig. 6. In vivo caspase selectivity by P49 and P35. (A) Cleavage sites. The P4–P1′ residues of P49 and P35 are compared with the initial processing sites of pro-Sf-caspase-1 and -2. (B) Anti-apoptotic activity. The capacity of plasmid-borne wild-type (wt) or mutated p49 and p35 to block virus-induced apoptosis was determined by marker rescue. The average ± standard deviation of triplicate transfections is reported as a percentage of the capacity of wild-type P35 to restore virus replication. (C and D) Processing of Sf-caspases. SF21 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wt or mutated P49 (lanes 1–4) or wt or mutated P35 (lanes 5–8), and infected 24 h later to induce apoptosis. Lysates (3.8 × 105 cell equiv) prepared 24 h after infection were subjected to immunoblot analysis with α-Sfcasp2 (C) or α-Sfcasp1 (D).
