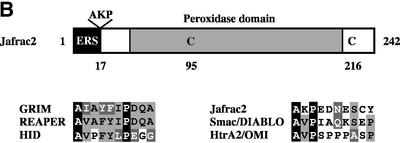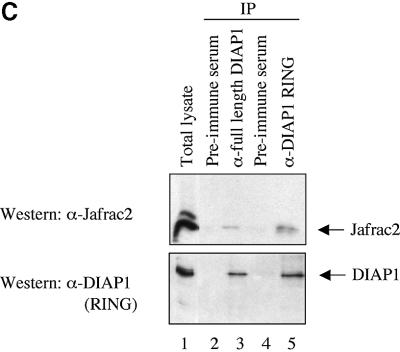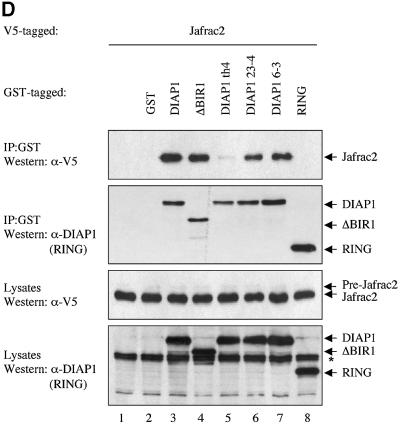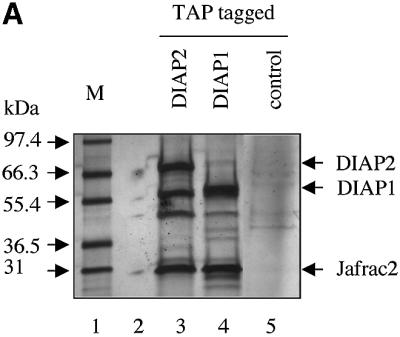
Fig. 1. Jafrac2 is an IAP-binding protein. (A) DIAP2 (3) and DIAP1 (4) but not an unrelated control protein (5) specifically co-purified a protein with an apparent molecular weight of 26 kDa (Jafrac2). Purified material was resolved by SDS–PAGE and visualized by silver staining. Molecular mass markers in kDa are shown (1). (2) is an empty lane. (B) Bar diagram representing the structure of Jafrac2 and the location of the AKP motif. ERS designates the ER targeting sequence. Cysteine residues important for the thioredoxin peroxidase activity of Jafrac2 are indicated. Lower panel: alignment of the N-terminal sequences of Rpr, Grim and Hid (left) and Jafrac2, Smac/DIABLO and HtrA2/Omi (right). Proteins were grouped based on the maturation by a methionine amino peptidase (left) and by proteolytic cleavage (right). Identical residues are shown in black, residues identical in two out of the three sequences are indicated in light grey, while residues with ≥60% similarity are shown in dark grey. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous Jafrac2 with endogenous DIAP1 from S2 cells. Jafrac2 was co-immunoprecipitated by anti-full-length (3) and anti-RING DIAP1 (5) antibodies, but not the pre-immune serum (2 and 4). (D) The BIR2 of DIAP1 is required for Jafrac2 binding. S2 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated combinations of constructs encoding Jafrac2-V5 and wild-type or mutant DIAP1–GST. DIAP1–GST was purified from cell lysates using gluthathione beads and associated Jafrac2 was detected by immunoblot analysis with anti-V5 antibodies (top panel). Effective DIAP1 purification was determined by immunoblotting the eluate with an anti-DIAP1 RING antibody (second panel). Expression of the indicated constructs was confirmed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (third and fourth panels). An asterisk denotes endogenous DIAP1.