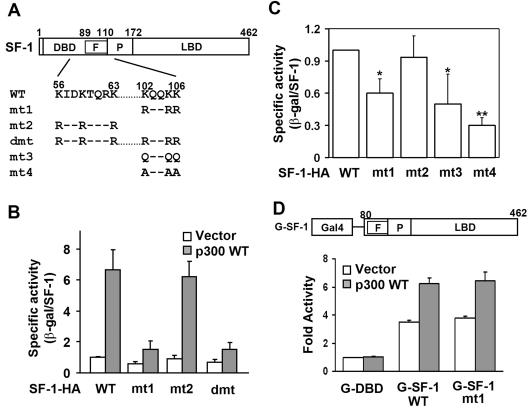
FIG. 4.
The KQQKK sequence is required for p300-potentiated activation and basal activity of SF-1. (A) Schematic representation of SF-1 constructs. The amino acid sequences of two potential acetylation sites are shown. Lys (K) residues were replaced with Arg (R), Gln (Q), or Ala (A) as indicated. (B) Lys-to-Arg mutation at the KQQKK motif of SF-1 (mt1) diminishes its p300-potentiated transcriptional activity. The specific activities of SF-1 were determined in the presence (p300 WT) or absence (Vector) of p300 in NIH 3T3 cells. (C) Mutation of K to Q or A at the KQQKK motif of SF-1 reduces its basal transcriptional activity. The specific activities of wild-type and mutated SF-1 expressed in NIH 3T3 cells are shown. *, P of <0.05, and **, P of <0.01, compared with wild-type SF-1-HA transfection, by Student's t test. (D) The KQQKK sequence is not required for full activation of SF-1 when linked to the DBD of Gal4 protein. Y1 cells were transfected with the 5×Gal4-tk-Luc reporter gene and expression plasmids for Gal4-DBD (G-DBD), wild-type Gal4-SF-1 (G-SF-1 WT), or mutated Gal4-SF-1 (G-SF-1 mt1). The transactivation activity (n-fold) of each protein relative to that of the G-DBD control is shown as mean ± standard deviation on the y axis. F, Ftz-F1 box; P, proline-rich domain; LBD, ligand-binding domain; WT, wild type; and β-gal, β-galactosidase.