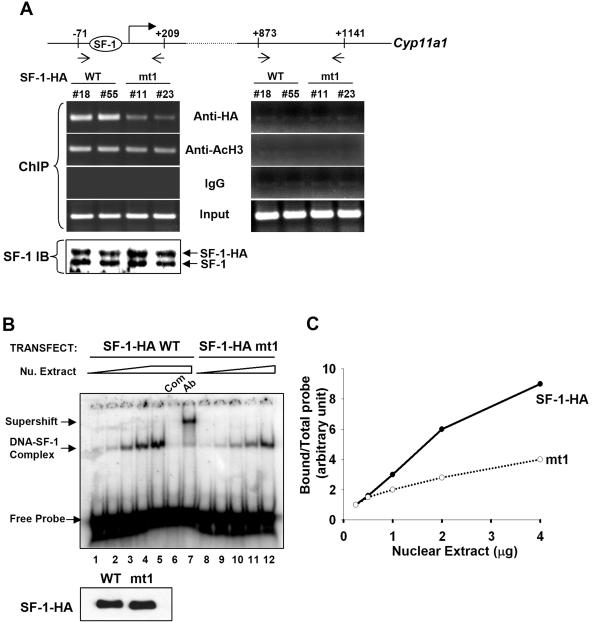
FIG. 5.
Mutation of the acetylation site in the Ftz-F1 box of SF-1 results in decreased binding to DNA. (A) ChIP. Soluble chromatin was prepared from stable Y1 cell clones expressing SF-1-HA (clones no. 18 and no. 55) and SF-1-HA mt1 (clones no. 11 and no. 23) and immunoprecipitated with antibodies against HA, acetyl-H3 (AcH3), or IgG control. DNA in the extracts was further analyzed by PCR using primers that cover the regions of nucleotide positions −71 to +209 or +873 to +1141 of the Cyp11a1 gene, as indicated. Protein expression levels of SF-1 in stable clones were determined by immunoblotting (IB) with antiserum against SF-1 (bottom). (B) Wild-type SF-1-HA (SF-1-HA WT) or mutated SF-1-HA (SF-1-HA mt1) was coexpressed with p300 in 293T cells prior to DNA binding and electrophoretic mobility shift assays. The DNA-SF-1 complex was formed with increasing amounts of nuclear (Nu.) extract (0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 μg). Com, competition with 100× unlabeled oligonucleotide; Ab, supershift with anti-HA antibody. The immunoblot with anti-HA antibody showing both WT and mt1 expressed at the same level is shown at bottom. The triangle and trapezoid denote increasing amounts of nuclear extracts. (C) The relative binding abilities of SF-1-HA WT and SF-1-HA mt1 are presented as the ratios of bound probe/total probe versus the amounts of nuclear extract.