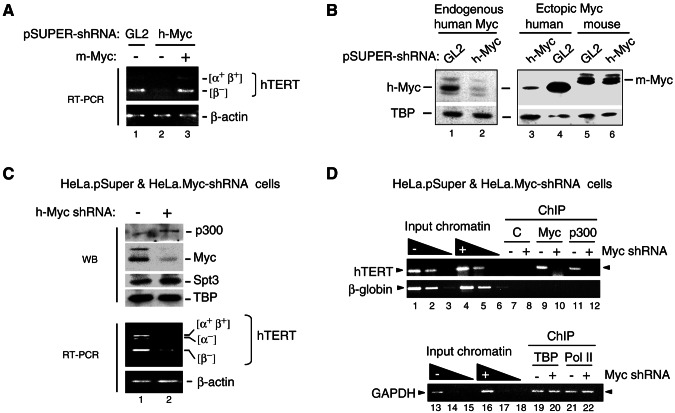
FIG. 8.
Myc is required for activation of the endogenous hTERT gene and for recruitment of p300 to the hTERT promoter in HeLa cells. (A) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with pSUPER vectors expressing shRNAs for luciferase (GL2) or human c-Myc (h-Myc) and either the mouse Myc (m-Myc) expression vector pCbS-Flag-Myc (lane 3) or its empty vector pCbS (lanes 1 and 2), and transcripts for hTERT and β-actin were analyzed by RT-PCR. Several hTERT splicing variants (α+ β+ and β−) are indicated. (B) HeLa cells were transfected as described above with vectors expressing GL2 or h-Myc shRNAs alone (lanes 1 and 2) or together with expression vectors for human Myc (h-Myc) (lanes 3 and 4) or mouse Flag-Myc (m-Myc) (lanes 5 and 6). After 72 h endogenous and ectopic human Myc (h-Myc) and ectopic mouse Myc (m-Myc) were analyzed by Western blotting with a Myc antibody and with the hTBP antibody. (C) HeLa.Myc-shRNA cells stably expressing the h-Myc shRNA (+) and HeLa.pSuper control cells (−) were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with p300, Myc, SPT3, and TBP antibodies (upper panels) and by RT-PCR (bottom panels). The hTERT splicing variants and β-actin transcripts are shown. (D) Equivalent amounts of chromatin from HeLa.Myc-shRNA and HeLa.pSuper control cells, which express (+) or not (−) Myc shRNA were immunoprecipitated (ChIP) with either rabbit serum (C, lanes 7 and 8), or specific antibodies to Myc (lanes 9 and 10) or p300 (lanes 11 and 12). The position of the hTERT promoter PCR fragment is indicated with an arrowhead. PCRs with dilutions of input chromatin from both cell lines are shown (lanes 1 to 6). A region in the third intron of the β-globin gene was amplified as background control. Chromatin precipitated with hTBP and RNA polymerase II antibodies and PCR amplified with GAPDH promoter primers is shown in lanes 19 to 22.