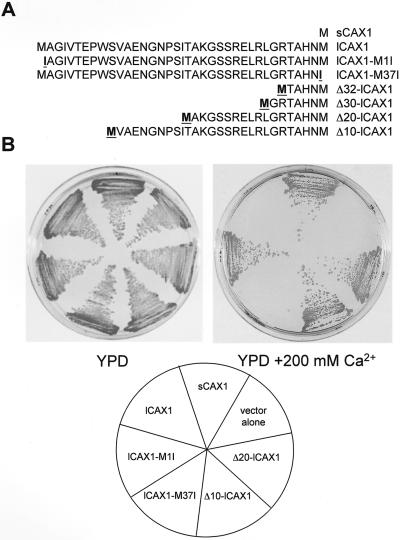
Figure 5.
The ability of lCAX1 mutants with structural alterations at the N-terminal tail to suppress the Ca2+-sensitive growth phenotype of K667 mutant yeast. A, Schematic representation of the first 37 amino acids of lCAX1 summarizing the point mutations and truncations that were generated. Highlighted Ile residues indicate a substitution from Met. Highlighted Met residues indicate the addition of a Met that was created to initiate translation following truncation. B, Growth analysis of K667 mutant yeast expressing sCAX1, lCAX1, lCAX1-M1I, lCAX1-M37I, Δ20-lCAX1, Δ10-lCAX1, and vector alone. The yeast strains were streaked onto either plates containing YPD alone or YPD supplemented with 200 mm CaCl2, then grown at 30°C for 2 d.