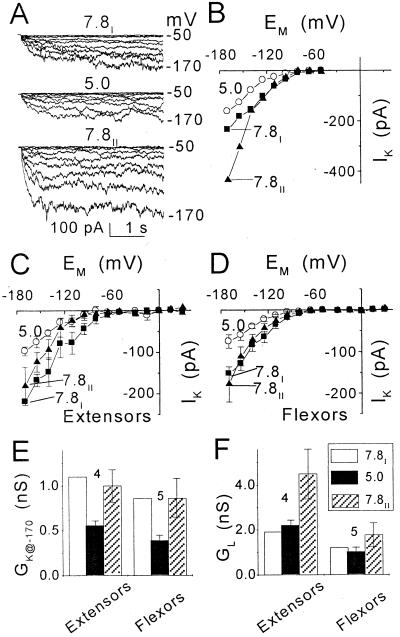
Figure 7.
The effect of external pH on membrane conductance at [K+]O of 200 mm (pipette solution: f). A, Inward currents in a flexor cell at the indicated pHs. Pulse protocol as in Figure 1A. Numbers at the right are the membrane potentials during the corresponding pulses. B, I-EM relationships of the time-dependent current records in A during consecutive treatments at pH 7.8 (7.8I), then at pH 5.0 and again at pH 7.8 (7.8II). C and D, I-EM relationships of the time-dependent currents (mean ± se), compared at the two pHs in the same cells: four extensors and five flexors (see “Materials and Methods” for details of averaging). The mean (±se) values of the extensors and flexors currents at pH 7.8 and −170 mV, used for the normalization and “restoration,” were 219 ± 55 pA and 153 ± 29 pA, respectively. E and F, Comparison of conductances (mean ± se, n), GK at −170 mV (GK@−170) and GL (between −80 and −170 mV), in the extensors and flexors of C and D, at the different pHs. Prior to averaging, GK@−170 at each pH was normalized to GK@−170 at pH 7.8I. The mean values used for normalization were 1.1 ± 0.2 nS in extensors and 0.8 ± 0.2 nS in flexors.