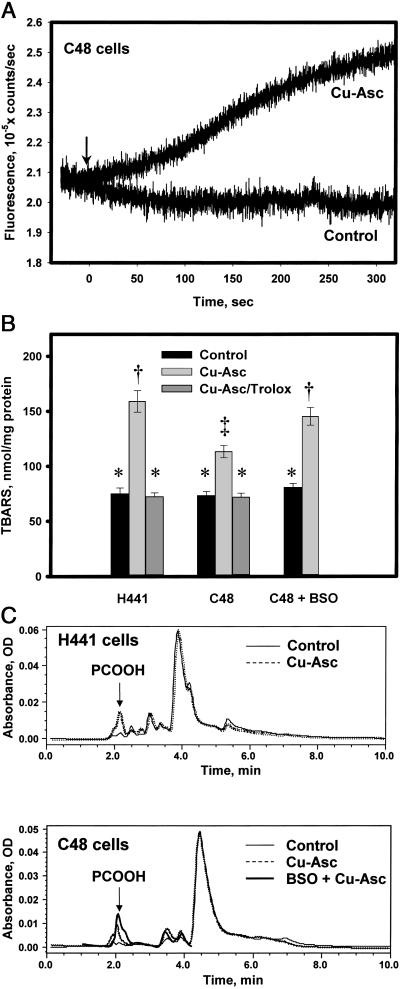
Figure 3.
Cellular lipid peroxidation with Cu-Asc. (A) Detection of •OH, generated by Cu-Asc, by a plasma membrane-localized probe (PE-3CCA) in C48 cells. A confluent monolayer of C48 cells on a plastic slide was labeled with the probe and fluorescence at 450 nm (excitation at 395 nm) was detected in real time. PE-3CCA fluorescence is shown with and without Cu-Asc addition (indicated by arrow). (B) Analysis of TBARS in lipid extracts of H441 or C48 cells with or without Cu-Asc exposure in the absence or presence of Trolox (50 μM) or C48 cells treated with BSO (10 μM) for 48 h before Cu-Asc exposure. Data are mean ± SEM for n = 3. Bars with different symbols (*, †, ‡) are significantly different (P < 0.05). (C) HPLC analysis for conjugated dienes (absorbance at 234 nm) in lipid extracts of H441 and C48 cells showing control (untreated) cells, Cu-Asc-treated cells (30 min at 37°C), and cells pretreated with BSO (48 h, 10 μM) before addition of Cu-Asc. The arrow indicates the retention time for the phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxide standard. The tracing for Cu-Asc plus BSO is terminated at 4 min because subsequent peaks seemed to be distorted by the BSO treatment.