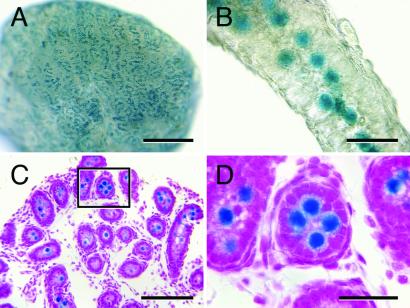
Figure 1.
MT-lacZ neonatal rat testis (2 dpp) stained with X-Gal to detect lacZ-encoded β-galactosidase activity. (A) Macroscopic image showing that lacZ expressing cells are evenly distributed in the neonatal rat testis. (B) Higher magnification image of an individual seminiferous tubule from the testis shown in A demonstrating that lacZ expressing cells are located in the center of the seminiferous tubule. (C) Histological analysis confirms that lacZ-expressing cells are located in the seminiferous tubule lumen, the characteristic location of gonocytes in neonatal testes. (D) Higher magnification of the seminiferous tubule boxed in C reveals the large size of gonocytes relative to other cells in the neonatal rat testis. Counterstain (C and D), hematoxylin and eosin. [Bars = 0.5 mm (A), 40 μm (B), 100 μm (C), and 30 μm (D).]