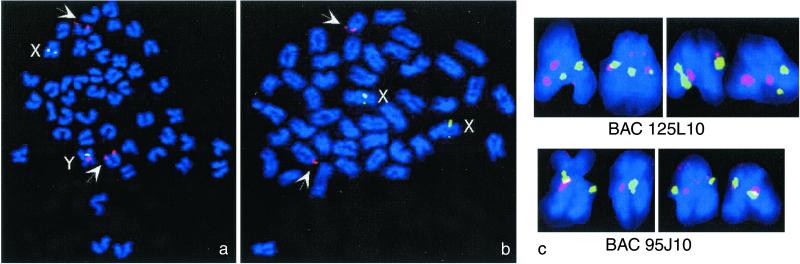
Figure 3.
Identification of the medaka Y chromosome: metaphases from male (a) and female (b) showing the hybridization signals of two BAC probes (15H17: DMRT1Y; 98C17: SL1). Note the presence of three hybridization spots for the BAC 15H17 in males as compared with the two spots in female (red signal). The additional fluorescence in situ hybridization signal in male is on the Y chromosome. The two relatively weak signals (arrows) in both male and female metaphase spreads represent the autosomal DMRT1 locus (linkage group 9). The SL1 marker containing BAC 98C17 detects both sex chromosomes (green signal). (c) Two highly enlarged XY chromosome pairs from two metaphases of male medaka showing hybridization to both sex chromosomes of BACs, which contain sequences flanking the Y-specific region on either side (95J10 and 125L10) (red signals). The SL1 marker containing BAC98C17 (green signals) was used to identify the sex chromosomes.