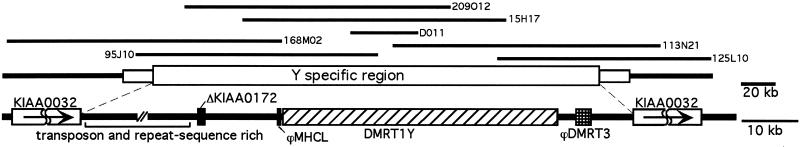
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the DMRT1Y-containing region. Lines above show the analyzed BAC and cosmid clones. Genes and sequences with predicted homology to known genes are shown as boxes: striped, DMRT1Y; hatched, ϕDMRT3; light gray, KIAA0032; black, ΔKIAA0172 and ϕMHCL. The region upstream of ΔKIAA0172 contains only repetitive DNA and sequences with similarity to transposable elements of various organisms. Two genes upstream of DMRT1, a myosin heavy chain like gene (MHCL) and an ankyrin repeat containing gene (orthologous to human KIAA0172), are part of the duplicated fragment from linkage group 9 on the Y. The duplicated Y-chromosomal copy of MHCL is, however, destroyed by insertion of a poseidon element, a non-long terminal repeat retroposon (40), in Southern medaka and additionally a TX-1-related transposon in Northern medaka. The Y-chromosomal version of KIAA0172 is corrupted by a deletion that takes out two exons. In addition, the 5′ part of the gene is missing, indicating the border of the duplicated fragment. In intron 4 of DMRT1Y an insertion has occurred. This insertion contains a duplicated copy of the putative medaka homologue of the human brain and testes antigen gene MAP1 that is located on medaka linkage group 19 (M.K., H. Mitani, A.S., and M.S., unpublished work). The Y-chromosomal copy of MAP1, however, has a frameshift mutation that leads to a prematurely terminated protein. Downstream of the Y-chromosomal DMRT1 a copy of DMRT3 is found. But its coding sequence is lacking the ATG start codon and it has several frameshifts. DMRT2, which is the next gene following DMRT3 on the autosomal cluster, is not found in the Y-specific region.