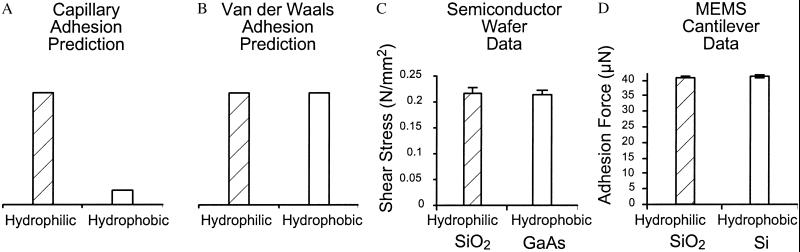
Fig 1.
Force of gecko setae on highly polarizable surfaces versus for surface hydrophobicity. (A) Wet adhesion prediction. (B) van der Waals prediction. (C) Results from toe on highly polarizable semiconductor wafer surfaces differing in hydrophobicity. (D) Results from single seta attaching to highly polarizable MEMS cantilevers differing in hydrophobicity. Note that geckos fail to adhere to hydrophobic, weakly polarizable surfaces [polytetrafluoroethylene where θ = 105° (25) and the dielectric constant, ɛ = 2.0 (23)]. Adhesion to hydrophilic and hydrophobic polarizable surfaces was similar. Therefore, we reject the hypothesis that wet, capillary interactions are necessary for gecko adhesion in favor of the van der Waals hypothesis.