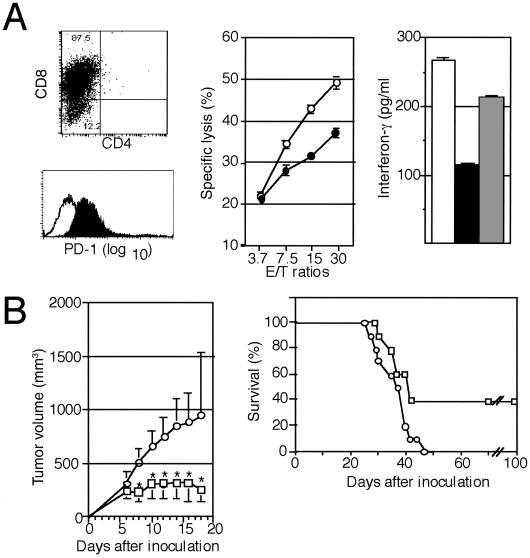
Fig 3.
Inhibition of the tumorigenesis of P815/PD-L1 cells by the injection with anti-PD-L1 mAb in vivo. (A Left) Syngeneic P815 tumor-specific T cells were generated in DBA/2 mice as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed for the expression of CD4, CD8, and PD-1. (Center) The CD8+ T cells were incubated with 51Cr-labeled P815 (○) or P815/PD-L1 (•) cells at varying effector-to-target ratios for 4 h, and the specific cytotoxicity was determined. The means and SE of triplicated cultures are indicated. (Right) The CD8+ T cells (2 × 106) were cocultured with 5 × 106 P815 (open bar) or P815/PD-L1 cells in the absence (solid bar) or presence (shaded bar) of anti-PD-L1 mAb F(ab′)2 (10 μg/ml) for 24 h, and IFN-γ in the culture supernatants was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The means and SE of triplicated cultures are indicated. (B) DBA/2 mice (10 mice per group) were inoculated s.c. with 3 × 106 P815/PD-L1 cells, and normal rat IgG (○) or anti-PD-L1 mAb (□) was injected on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 at 0.1 mg per mouse each time. The mean tumor volumes and SE of 10 mice (Left) as well as their survival rates (Right) are indicated. *, P < 0.01 by Student's t test.