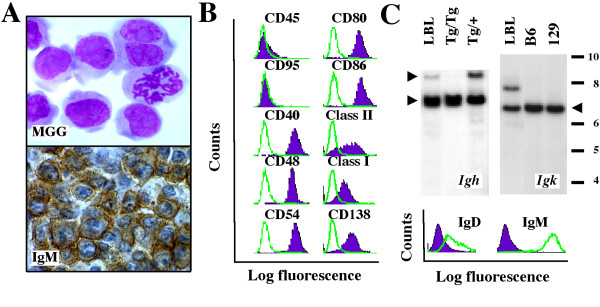
Figure 1.
Features of iMycEμ-1 cells. A, cytofuge specimen of cultured cells stained according to May-Grünwald-Giemsa (top). Tissue section of the LBL from which the cell line was derived after immunostaining for μ H-chain (bottom). B, B-cell surface marker expression evaluated by FACS in cells treated with specific antibodies (purple histograms) or isotype controls (green lines). C, H/L rearrangements and surface Ig expression. Southern blots of Igh (top left) and Igk (top right) rearrangements of the LBL from which the cell line was derived. Included as control is liver DNA from homozygous (Tg/Tg) or heterozygous (Tg/+) transgenic iMycEμ mice (left panel) or inbred C57BL/6 and 129SvJ mice (right panel). Recombination at the Igh locus was detected by the reduction of the normal, H chain-encoding upper fragment (upper arrowhead) in the face of comparable amounts of the mutated, MycHis-harboring lower fragment (lower arrowhead). Thus, the 6.2 kb long upper fragment was diminished in the LBL compared to the Tg/+ sample (and absent, as expected, in the Tg/Tg sample), whereas the MycHis-harboring lower fragment was comparable. The MycHis-bearing Igh locus cannot encode H chain because of the gene insertion. Recombination at the Igκ locus resulted in an enlarged fragment (~7.8 kb) compared to the germ line fragment that is indicated by the arrowhead pointing left. Detection of surface IgMhiIgDlow using FACS analysis (bottom).