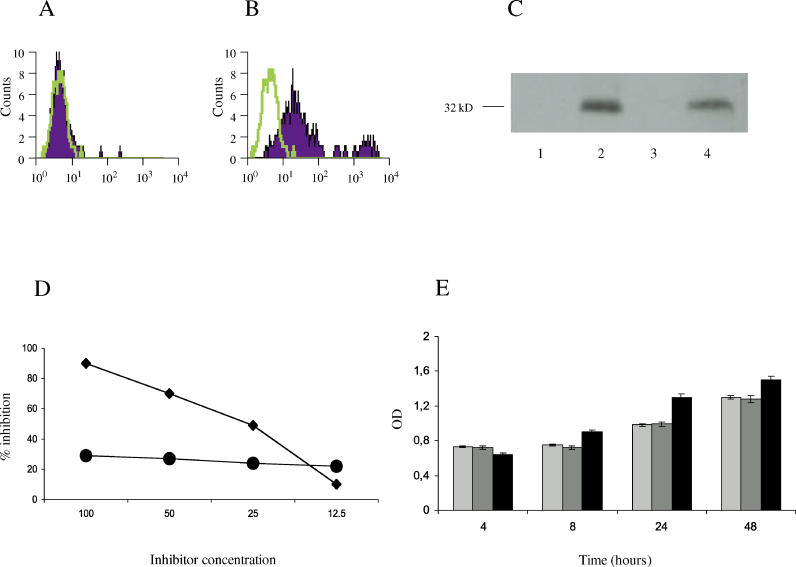
Figure 1. Anti-hCMV Antibodies Recognize the NAG-2 Receptor on Dermal Fibroblasts and Do Not Affect Cell Proliferation.
(A and B) FACS analysis of the binding of antibodies to normal human fibroblasts: antibodies affinity purified against the irrelevant peptide from sera of SSc patients (A) and antibodies affinity purified against the UL94 peptide from the same sera (B). Percentage of positive cells is 7% (A) and 83 % (B), respectively.
(C) Anti-peptide antibodies react with the NAG-2 molecule. Lysates from human dermal fibroblasts were immunoprecipitated with a rabbit affinity purified anti-UL94 peptide antibody crosslinked to sepharose. Immunoprecipitates were resolved in SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellullose. Blots were incubated with pre-immune rabbit antiserum (lane 1), rabbit anti-UL94 peptide antibody (lane 2), affinity purified antibodies directed against the irrelevant control peptide isolated from patients with SSc (lane 3), and anti-UL94 peptide antibodies purified from the sera of the same patients (lane 4).
(D) Binding of affinity purified antibodies against the UL94 peptide to fibroblasts is specifically inhibited by the UL94 peptide (diamonds) but not by an irrelevant control peptide (circles). Data represent percent of inhibition; inhibitor concentration (horizontal axis) is in micrograms per milliliter.
(E) Fibroblasts incubated with anti-hCMV antibodies normally proliferate. Shown are proliferation levels for fibroblasts incubated for various intervals of time with medium alone (light grey bars), with affinity purified antibodies directed against the irrelevant control peptide (dark grey bars), or with affinity purified antibodies against the UL94 peptide (black bars). OD, optical density at 570 nm.