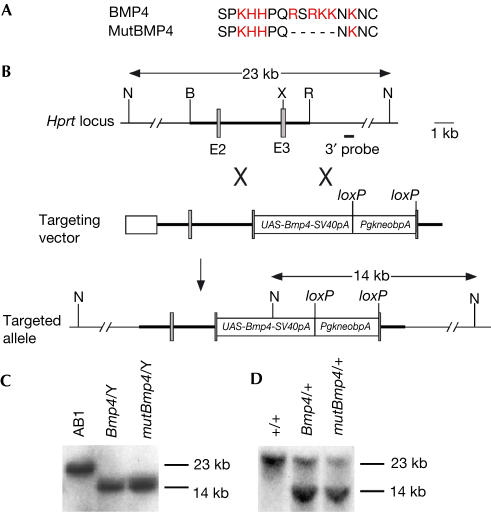
Figure 1.
Generation of UAS-Bmp4 and UAS-mutBmp4 knockin mice. (A) The N-terminal amino-acid sequence preceding the first cysteine of the mature BMP4 protein is rich in basic amino acids (red). The mutant form of BMP4 (mutBMP4) used in this study has an in-frame five-amino-acid deletion. (B) Gene targeting strategy. UAS-Bmp4 (or UAS-mutBmp4) was inserted into exon 3 (E3) of the Hprt locus. The shaded boxes denote exons, and the thick line represents the homology used for gene targeting. B, BamHI; N, NcoI; R, EcoRI; TK, thymidine kinase expression cassette; X, XhoI. (C) Southern blot analysis of NcoI-digested DNA from control (AB1) and UAS-Bmp4 (Bmp4/Y) and UAS-mutBmp4 (mutBmp4/Y) targeted XY ES cell clones. Only one mutant band is detected because the Hprt gene is located on the X chromosome. (D) Southern hybridization of NcoI-digested tail DNA isolated from control (+/+) and agouti-pigmented daughters of male chimaeras (Bmp4/+, UAS-Bmp4 heterozygote; mutBmp4/+, UAS-mutBmp4 heterozygote).