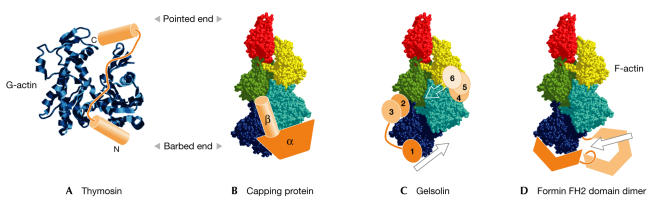
Figure 2.
Schematic representations of the sequestering and capping of actin by thymosin, capping protein, gelsolin and formins. (A) Globular actin (G-actin; blue ribbon) is 'capped' at the top and bottom by the N- and C-terminal helices of thymosin (orange), which are connected by an unstructured loop. (B) The capping protein β-tentacle forms an interface between three actin subunits at the barbed end of a short filament of five actin monomers (shown in space-filling representation). The α-tentacle and the remainder of the β-capping protein are in an equivalent position on the rear side of the filament. (C) The six subunits of gelsolin are coloured in orange and are arranged in their approximate positions on the filament. The planes of severing are indicated by arrows. (D) The formin homology 2 (FH2) domain dimer is represented as dark and light orange, with the darker subunit bound to the dark blue actin monomer at the barbed end of the filament, and the lighter subunit hinged down via the linker and lasso-and-post structures to allow a new actin monomer to be added (arrow).