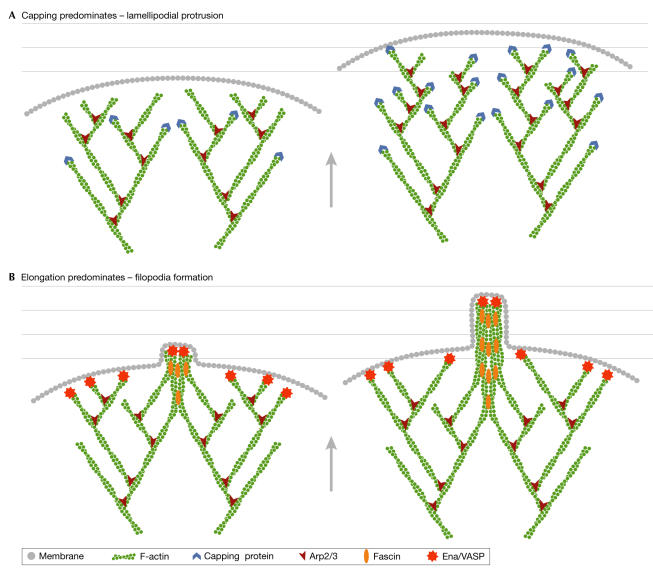
Figure 3.
A schematic representation of the mechanisms of lamellipodia and filopodia formation at the leading edge of cells. (A) If capping activity predominates, then many short branched filaments are formed into a broad dendritic network. (B) If capping activity is reduced and/or elongation is favoured, longer filaments are formed that are then bundled into filopodia by proteins, such as fascin. Arp2/3, actin-related protein 2/3; Ena/VASP, Enabled/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein.