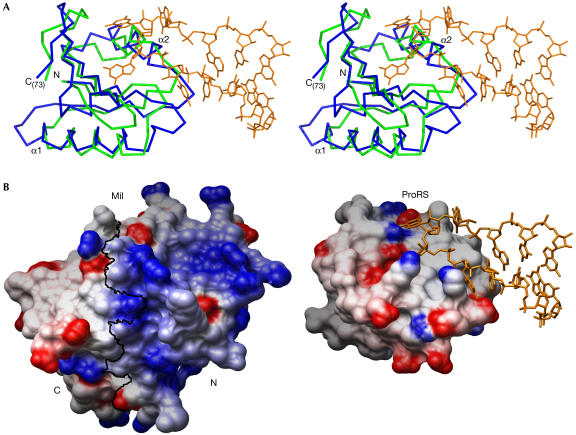
Figure 3.
Structural similarity between Mil and anticodon-binding domains. (A) The structures of Mil and the anticodon-binding domain of the prolyl-tRNA synthetase (ProRS) from Thermus thermophilus complexed with its tRNA-Pro(CGG) substrate (PDB ID 1H4S) were superposed. The proteins are represented as Cα traces in green (Mil) and blue (ProRS). Only the aligned residues are shown, namely Met1 to Ile73 for Mil and Val290 to Leu372 for ProRS. The Pro-tRNA (nucleotides 30–40) is in orange. (B) Electrostatic potential of Mil (left) and the anticodon-binding domain of ProRS (right) mapped on their respective molecular surfaces, with charges coloured in the range of +10 kT/e (blue) to −10 kT/e (red). Electrostatic calculations were carried out with the program delphi (Sharp & Honig, 1990) and the figure prepared with Chimera (Huang et al, 1996). A black line marks the boundary between Mil N- and C-terminal halves, as defined in Fig 2B. Both proteins are shown in the same orientation on superposition, as in (A). Nucleotides 30–40 of the Pro-tRNA are represented in orange.