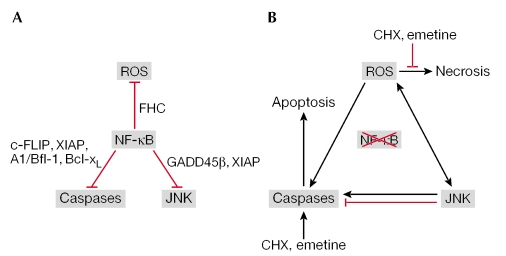
Figure 1.
A model for nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent survival signals. (A) Under normal conditions, NF-κB inhibits potentially apoptotic and necrotic signalling cascades, caspases that are induced by tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). (B) Under conditions in which NF-κB activation is blocked, three pro-apoptotic and necrotic signalling cascades are activated and amplify each other, which results in apoptosis or necrosis in a context-dependent manner. In the presence of a protein-synthesis inhibitor, such as cycloheximide (CHX) or emetine, TNF-α preferentially induces apoptosis. The black and red lines indicate positive and negative regulation, respectively.