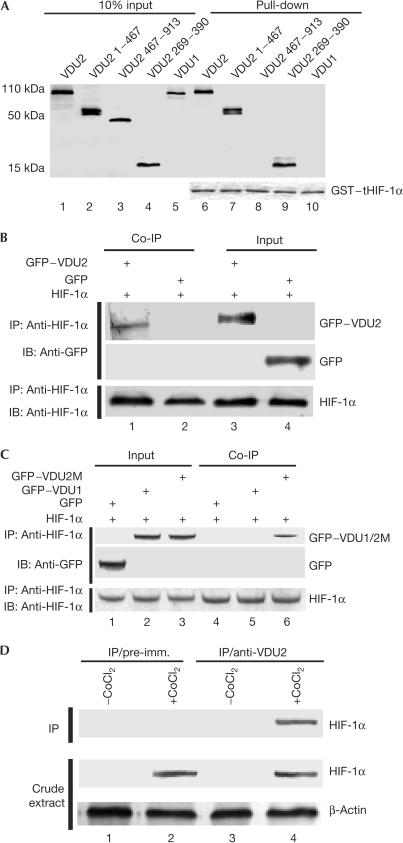
Figure 1.
VDU2, but not VDU1, interacts with HIF-1α. (A) GST pull-down assay for mapping the HIF-1α–VDU2 interaction. In vitro-translated VDU2, VDU2 1–467, VDU2 467–913, VDU2 269–390 and VDU1 proteins were incubated with GST–tHIF-1α (530–826) and the bound proteins were eluted and analysed using SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Equal loading of GST fusion proteins is demonstrated in the lower panel. (B) In vivo co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of HIF-1α with GFP–VDU2. Lysates prepared from COS-7 cells transfected with pCEP4–HIF-1α and pEGFP–C3 or pEGFP–C3–VDU2 were subjected to IP with anti-HIF-1α antibody followed by anti-GFP immunoblotting (IB). (C) In vivo Co-IP of HIF-1α with GFP–VDU1 or GFP–VDU2M-C154A. Lysates prepared from COS-7 cells transfected with pCEP4–HIF-1α plus pEGFP–C3, pEGFP–C3–VDU1 or pEGFP–C3–VDU2M-C154A were subjected to IP with anti-HIF-1α antibody followed by anti-GFP IB. (D) Interaction between endogenous HIF-1α and VDU2. The top panel shows a western blot of control IP with the pre-immune serum (lanes 1,2) and IP with VDU2 antibody (lanes 3,4) from HeLa cells untreated (lanes 1,3) or treated with CoCl2 (lanes 2,4). The middle and bottom panels show blots of cell extracts by anti-HIF-1α and anti-β-actin antibody, respectively.