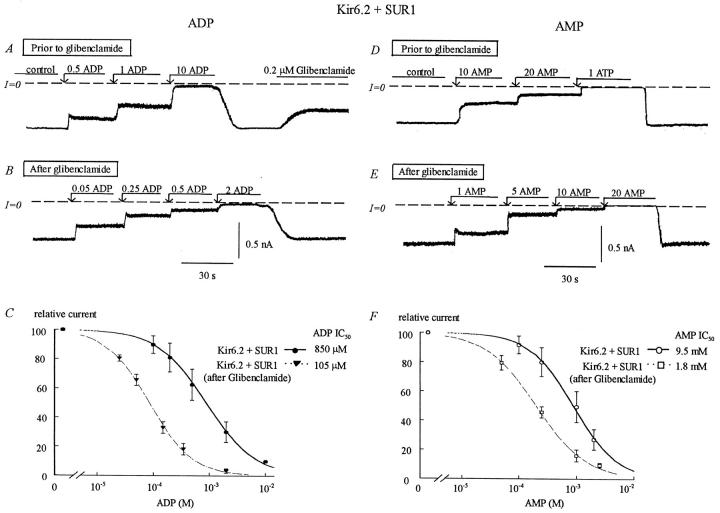
FIGURE 9.
Effects of glibenclamide on the ADP and AMP sensitivity of wild-type Kir6.2 + SUR1. The left and right sides of the figure show that glibenclamide induces an increase in sensitivity of wild-type Kir6.2+SUR1 to both ADP and AMP, respectively. (A) Inward currents were suppressed by increasing concentrations of ADP, with the IC50 near 1 mM. Glibenclamide (200 nM) was then added after removal of ATP. (B) After glibenclamide, the ADP sensitivity increased, with the IC50 near 100 μM. (C) Plot of channel ADP sensitivity for Kir6.2+SUR1 before (•) and after (▾) glibenclamide. In this case, fit of the data points yielded k = 850 μM before glibenclamide (n = 5) and k = 105 μM after glibenclamide for (▾) (n = 5). (D) Inward currents were suppressed by increasing concentrations of AMP, with the IC50 near 10 mM. (E) After glibenclamide, the AMP sensitivity increased with the IC50 near 2 mM. (F) Plot of channel AMP sensitivity for Kir6.2+SUR1 before (○) and after (□) glibenclamide. In this case, fit of the data points yielded k = 9.5 mM before glibenclamide (n = 5) and k = 1.8 mM after glibenclamide (n = 5).