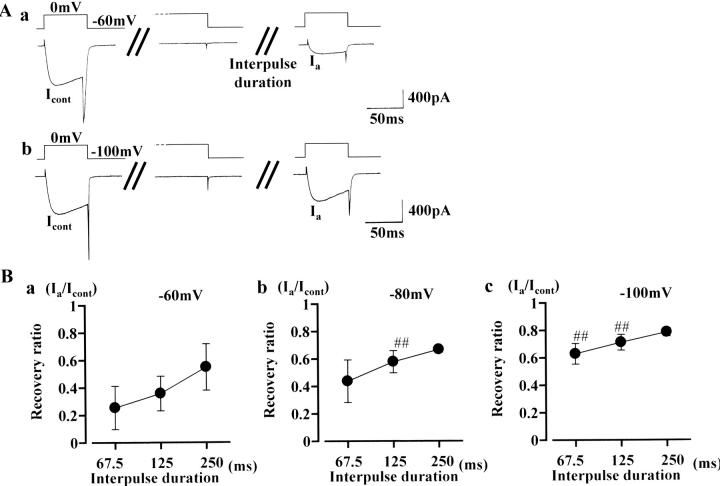
FIGURE 2.
Recovery time course from inactivation caused by a conditioning depolarization at 0 mV. After observing a control test current (at 0 mV), the cell membrane was clamped at 0 mV for 4 s. Subsequently, the same test step was again applied after an interpulse duration of 62.5, 125, or 250 ms. Representative current traces (with an interpulse duration of 125 ms) are shown in A. The interpulse potential used was −60 mV in a and −100 mV in b. In B, each point represents the mean value of time-dependent recovery (n = 13): recovery is expressed as percentage of the control current amplitude recorded before the conditioning depolarization to 0 mV (4 s). Bars, SD. The interpulse potential was −60 mV in a, −80 mV in b, and −100 mV in c. Double sharps (##) indicate data points that differ significantly from those in a (ANOVA, P < 0.01).