FIGURE 5.
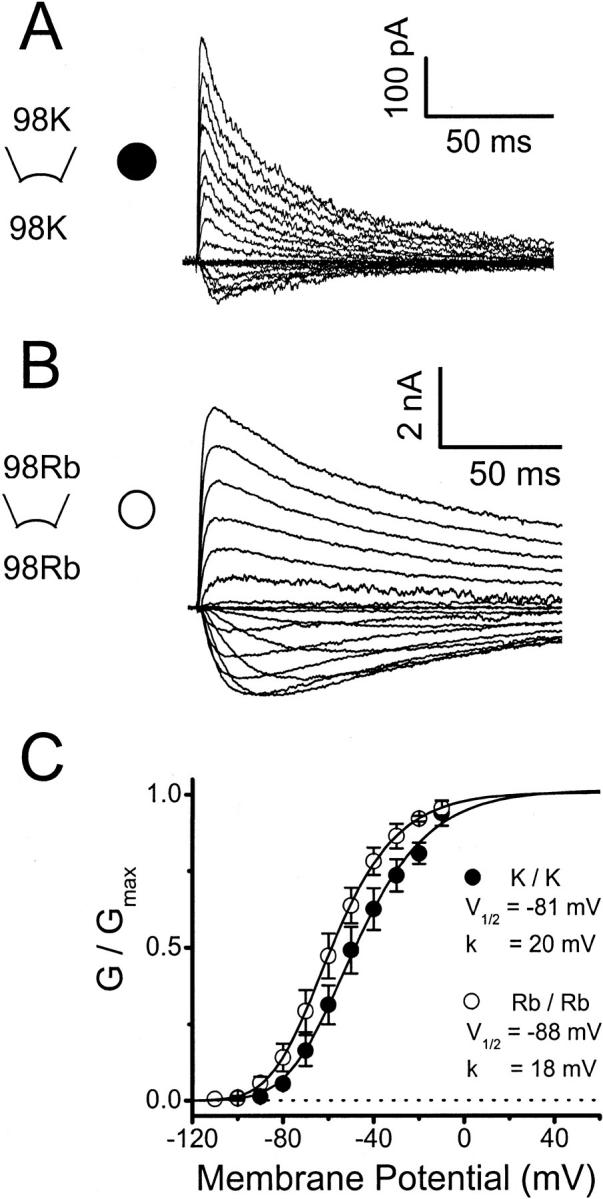
Peak conductance–voltage relation of Kv4.1 channels under symmetrical ionic conditions. (A) and (B) Kv4.1 K+ and Rb+ currents evoked by step depolarizations to various voltages ranging between −100 and +60 mV in 10-mV intervals. The holding potential was −100 mV. In both instances the currents were recorded from inside-out patches exposed to symmetrical 98 mM K+ or 98 mM Rb+. The reversal potentials under these conditions were −0.5 ± 0.9 mV and −0.6 ± 1.0 mV, in symmetrical K+ or symmetrical Rb+, respectively. (C) Normalized peak conductance-voltage relation (Materials and Methods). Lines are the best-fit fourth-order Boltzmann functions (Materials and Methods) with the parameters indicated in the graph. The graphically interpolated voltages that activate 50% of the peak conductance (VG=50%) were −50 mV and −60 mV in symmetrical K+ and symmetrical Rb+, respectively. Symbols are the means from three to six experiments. From pooling the best-fit parameters extracted from these experiments the mean V1/2 values were −78 ± 3 mV and −86 ± 3 mV in symmetrical K+ and symmetrical Rb+, respectively; and the mean k values were 18 ± 1 mV and 17 ± 1 mV in symmetrical K+ and symmetrical Rb+, respectively. The analysis of a limited number of corrected activation curves (n = 3, Materials and Methods) generated more variable curves but similar values of the extracted activation parameters: the mean V1/2 values were −78 ± 3 mV and −83 ± 4 mV in symmetrical K+ and symmetrical Rb+, respectively; and the mean k values were 17 ± 2 mV and 21 ± 2 mV in symmetrical K+ and symmetrical Rb+, respectively.
