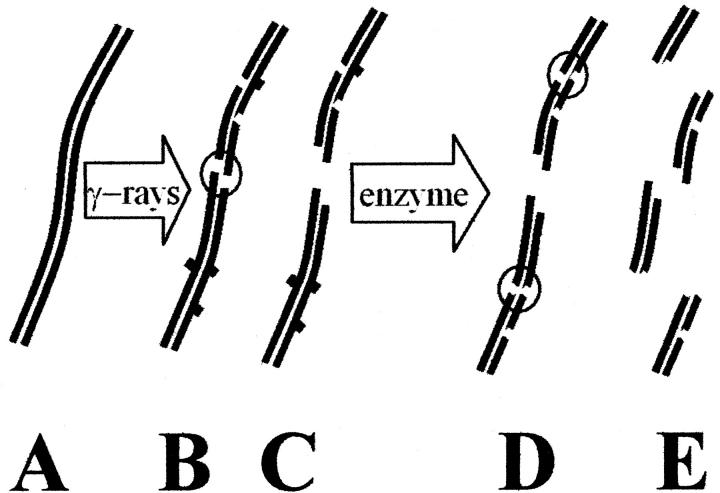
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of the induction of frank double-strand breaks and other bilateral clustered damages in DNA. Ionizing radiation, such as γ-rays, generates hydroxyl radicals and other reactive species that attack undamaged DNA (A), forming frank single-strand breaks (— —) and damaged bases (— ▪ —), as shown in (B). Multiple closely-spaced breaks involving opposing strands result in double-strand breaks (shown within a circle) and spawn two smaller DNA molecules (C). Subsequent treatments with a damage-specific enzyme result in the generation of additional single-strand breaks (D), yielding additional double-strand breaks if the damaged bases are closely spaced or if a damaged base is located near a single-strand break on the opposing strand. These double-strand breaks result in the generation of additional, smaller double-stranded DNA fragments (E). Isolated single-strand breaks or damaged bases, which are actually more numerous than clustered damages, do not generate increased numbers of smaller double-stranded DNA molecules.