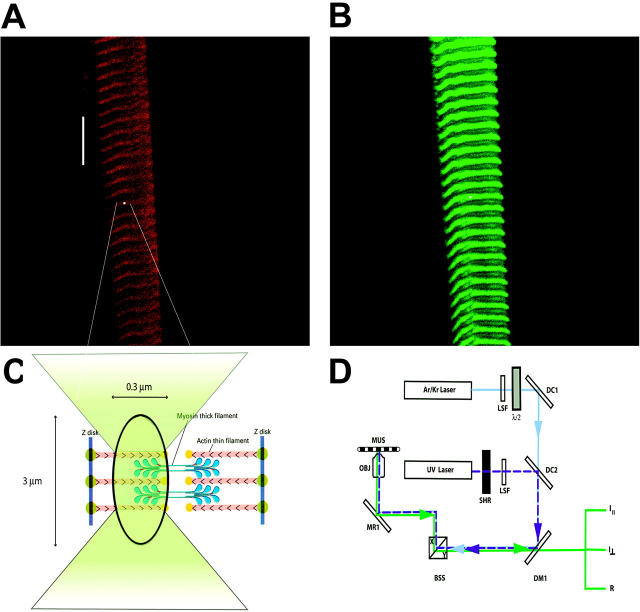
FIGURE 1.
Method of measuring anisotropy of fluorescence. Approximately 1% of myosin in a fiber is labeled with LC1-IATR, LC3-IATR, or RLC-Alexa488. (A) Fiber viewed through rhodamine filter set (long pass λ > 590 nm). The white spot indicates the position of the laser beam. Bar, 10 μm. (B) The same fiber viewed through fluorescein filter set (band pass 515 < λ < 565 nm). (C) Magnified view of the focused laser spot shown in A. (D) Simplified schematic diagram of the experimental setup. 568-nm light from Ar/Kr laser (Series 34, Omnichrome, Chino, CA) is selected by the line selection filter (LSF) to excite rhodamine. Polarization of the laser beam is rotated by λ/2 plate (mica retarder, model WRM 021, Melles Griot, Irvine, CA) and directed by the dichroic mirror DM1 and mirror MR1 onto an objective (OBJ). The UV beam of an argon laser (Enterprise, Coherent, Palo Alto, CA) operating at 364 nm (dark blue dashed line) is used to photolyze caged nucleotide. The UV light is admitted by the shutter (SHR) (Vincent Associates, Uniblitz T132, Rochester, NY). Dichroic combiner 2 (DC2) merges the UV and visible beams. Objective (OBJ, 40×, NA 1.2, water immersion) focuses the exciting light on the muscle (MUS) mounted on a stage of a microscope (Axiovert 135, Zeiss, Thornwood, NY). The objective collects fluorescent light and projects it to the photomultipliers. Mirrors of the beam scanner (BSS) are kept fixed at X = 0, Y = 0 position.