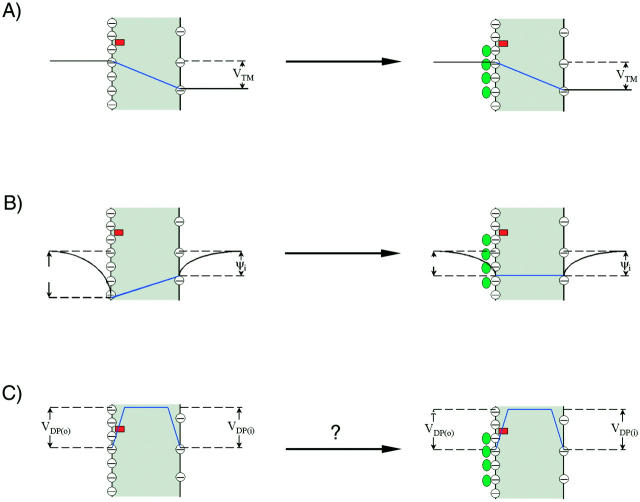
FIGURE 1.
Effect of extracellular cations on the potential profile across a cell plasma membrane. The dye chromophores (red rectangle) is sensing the electric field (blue line) generated by transmembrane potential (VTM) (A), the difference between the external surface potential (ψo) and internal surface potential (ψi) (B), and the dipole potential at the outer surface (VDP(o)) (C). We define all potential differences as potential inside minus potential outside. When the negative charges on the outer surface are neutralized and bound by cations (green oval), the equilibrium values of VTM is unchanged. However, the ψo is reduced, leading to an increase in intramembrane potential across the membrane, although ψi is unchanged. The effect of divalent cation binding on dipole potential is relatively small, especially at the concentrations used in this study. Therefore, the change in intramembrane potential, 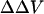 , which is calculated from Eq. 7
, which is calculated from Eq. 7 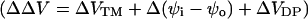 , is approximately equal to −Δψo.
, is approximately equal to −Δψo.