TABLE 1.
Electronic transition energies of WT-PYP, E46Q, and L-PYP
(a) 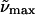 (λmax) buffer 298K (λmax) buffer 298K |
(b) 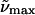 (λmax) gly/buffer 298K (λmax) gly/buffer 298K |
(c) 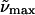 (λmax) gly/buffer 77K (λmax) gly/buffer 77K |
(d) 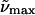 (λmax) gly/buffer 77K (λmax) gly/buffer 77K |
(e) 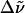 (a)–(b) (a)–(b) |
(f) 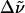 (a)–(c) [(a)–(d)] (a)–(c) [(a)–(d)] |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT-PYP | 22420 (446) | 22320 (448) | 22420 (446) | 22520 (444) | +100 | 0 [−100] |
| E46Q | 21740 (460) | 21650 (462) | 21790 (459) | 21980 (455) | +90 | 50 [−240] |
| L-PYP | 22520 (444) | 22420 (446) | 22520 (444) | 22520 (444) | +100 | 0 [0] |
All absorption maxima are reported in wavenumbers. The values in nanometers are given in parentheses. Experimental conditions: (a) Room temperature in Tris-HCl buffer at pH 7.5. (b) Room temperature in Tris-HCl buffer and 66% w:v glycerol solution. (c) 77 K glycerol-buffer glass before illumination with blue light (see Experimental). (d) 77 K glycerol-buffer glass following illumination with blue light. (e) Difference in energy between the absorption maxima in Tris-HCl buffer versus glycerol-buffer solution at room temperature. (f) Difference in energy between the absorption maxima in the glycerol-buffer glasses at 77 K versus in buffer solution at room temperature, before and after illumination with blue light.
