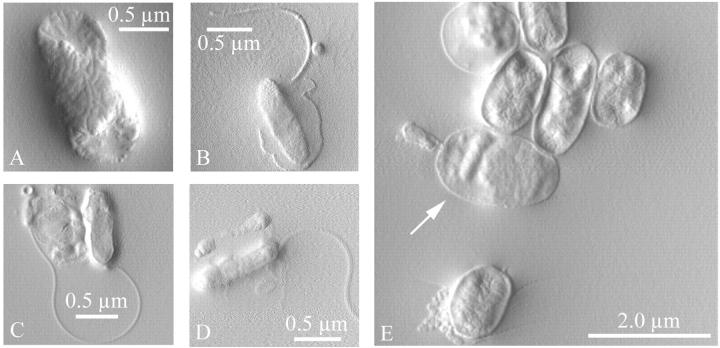
FIGURE 2.
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and invaded and uninvaded prey E. coli were imaged by atomic force microscopy in tapping mode (amplitude image). Bacteria were rinsed and dried on a smooth mica surface before imaging. (A) The prey E. coli, (B–D) the predator Bdellovibrio, and (E) invaded prey cells (bdelloplasts) were all observed. The arrow in E indicates a bdelloplast inside of which the predator was visible; a second predator was seen attached to the external surface of the cell. Another bdelloplast was visible at the top left, identified by its roundness, bumpy shape, and smooth surface texture.