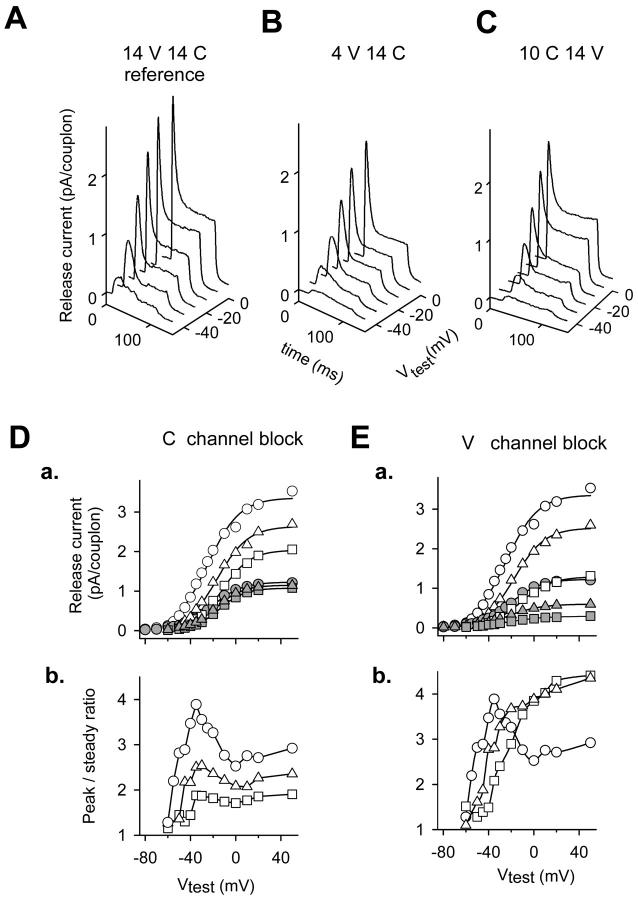
FIGURE 6.
Simulations; selective blockade of V- and C-channels. Top, Simulated release currents corrected for depletion for three conditions. (A) Reference, 14 channel couplon, with all C- and V-channels available. (B) Block of V-channels; 4 V-channels and 14 C-channels available. (C) Block of C-channels; 10 C-channels and 14 V-channels available. (D) a, Peak and steady release currents for all (circles), 10 (triangles), or seven (squares) C-channels available. The larger plot in each pair corresponding to the three conditions represents peak currents (unfilled symbols), the smaller steady currents (solid symbols). Fit parameters for 14C and 14V: maximum release current (MRC) = 3.36 pA/couplon, V* = −24.7 mV, and k = 14.05 mV for the peak current, MRC = 1.23 pA/couplon, V* = −21.3 mV, and k = 13.4 mV for the steady current. Fit parameters for 10C and 14V: MRC = 2.64 pA/couplon, V* = −16.2 mV, and k = 13.6 mV for the peak current; MRC = 1.15 pA/couplon, V* = −17.6 mV, and k = 11.9 mV for the steady current. Fit parameters for 7C and 14V: MRC = 2.04 pA/couplon, V* = −12.2 mV, k = 12.5 mV for the peak, and MRC = 1.08 pA/couplon, V* = −14.7 mV, and k = 11.3 mV for the steady current. b, Simulated voltage dependence of peak/steady ratio, with the same symbol code. (E) a, Peak and steady release currents for all (circles), four (triangles), or one V-channel available (squares). Fit parameters for 14C and 14V: same as in D a. For fit parameters 14C and 4V: MRC = 2.56 pA/couplon, V* = −17.2 mV, and k = 13.4 mV for the peak current; and MRC = 0.60 pA/couplon, V* = −23.0 mV, and k = 14.7 mV for the steady current. Fit parameters for 14C and 1V: MRC = 1.30 pA/couplon, V* = −11.8 mV, and k = 13.6 mV for the peak current; and MRC = 0.29 pA/couplon, V* = −22.9 mV, and k = 15.7 mV for the steady current. b, Peak/steady voltage dependence calculated from the values in a (same symbol code). Simulations were carried out with parameter values of Stern et al. (1997).