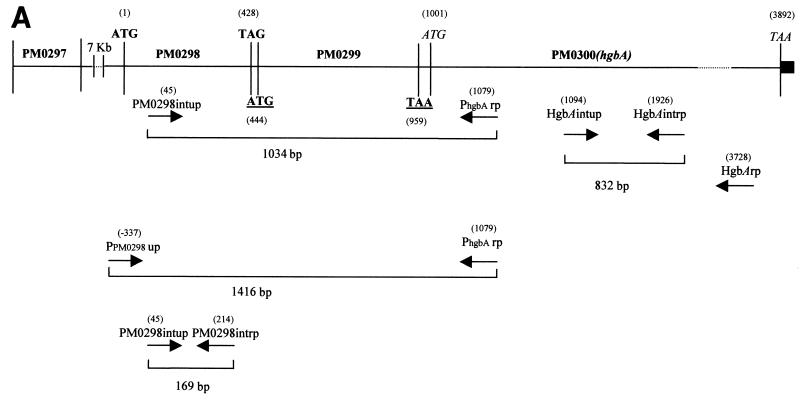
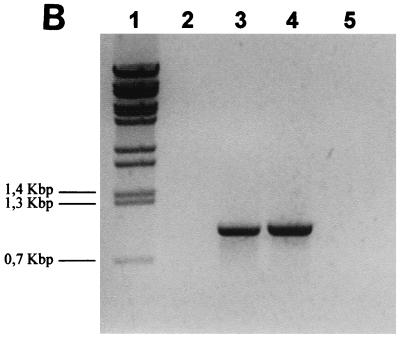
FIG. 1.
(A) Genetic organization of the P. multocida chromosomal region containing the PM0298-PM0299-PM0300 (hgbA) transcriptional unit. The translational start and stop codons for the PM0298, PM0299, and PM0300 ORFs are indicated by boldface type, by boldface type and underlining, and by italics, respectively. The positions of primers (Table 2) used to show the existence of a single mRNA by RT-PCR, as well as in the several constructions used in this study, are indicated. The numbers in parentheses indicate the positions with reference to the ORF PM0298 translational start point. The location of ORF PM0297 immediately upstream of PM0298 is also shown. The solid box downstream of ORF PM0300 (hgbA) represents the putative rho-independent transcriptional terminator of the operon. (B) RT-PCR analysis of the PM0298-PM0299-PM0300 (hgbA) transcript in P. multocida cells performed with PM0298intup and PhgbArp as the upper and lower primers, respectively, in the presence of RNA (lane 3). As a positive control, the PCR fragment obtained when P. multocida chromosomal DNA was used as the template (lane 4) was also examined. The negative controls were a preparation containing RNA template but no RT (lane 2) and a preparation lacking both RNA and DNA (lane 5). Lane 1 contained BstEII-digested λ DNA employed as the molecular size marker.