FIGURE 2.
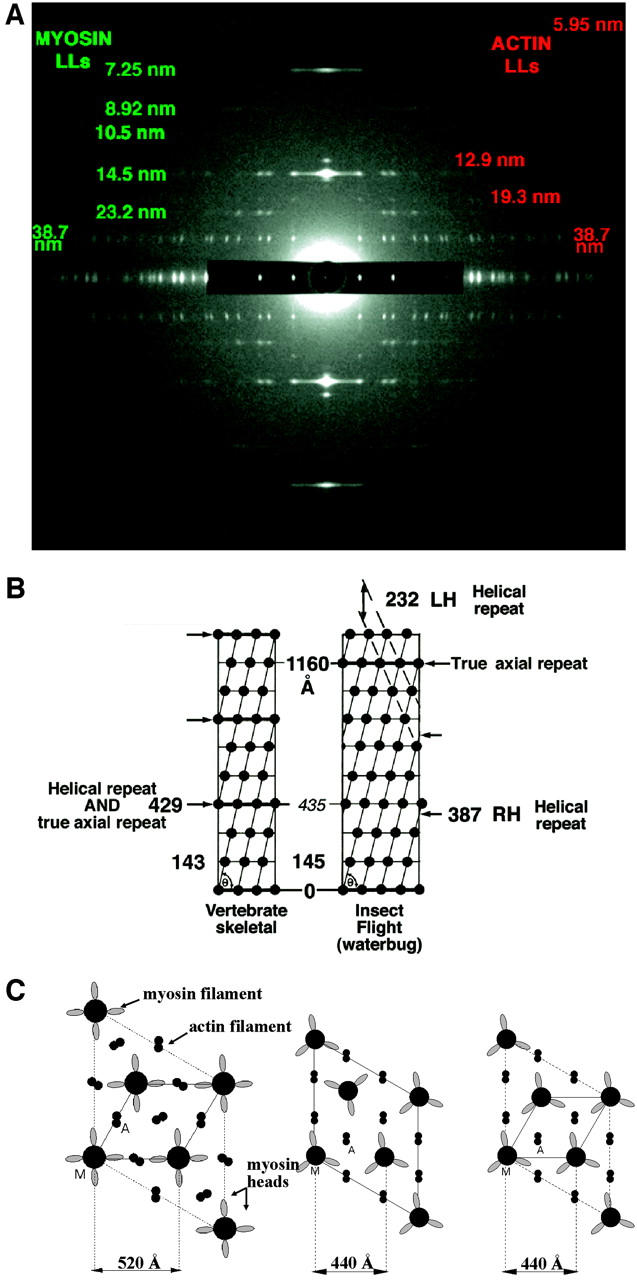
(a) The full relaxed insect low-angle x-ray diffraction pattern, showing 20 layer-lines, based on a 116-nm repeat, and ∼468 Bragg reflections. This pattern is obtained from relaxed bundles of glycerinated flight muscle from the waterbug Lethocerus indicus in the Mg-ATP relaxed state. (b) Surface helical net for vertebrate skeletal and IFM thick filaments comparing the helical repeat and the true axial repeat of the two structures. Rotation from crown to crown is 40° in vertebrate skeletal muscle and 33.75° in IFM. Vertebrate skeletal muscle has threefold rotational symmetry and IFM has fourfold. (c) Unit cell in transverse view for IFM, frog, and fish (from left to right, respectively) and their lattice spacings (A is actin filament, M is myosin filament). IFM and fish have a simple lattice, whereas frog has a superlattice with the myosin filaments not in rotational register.
