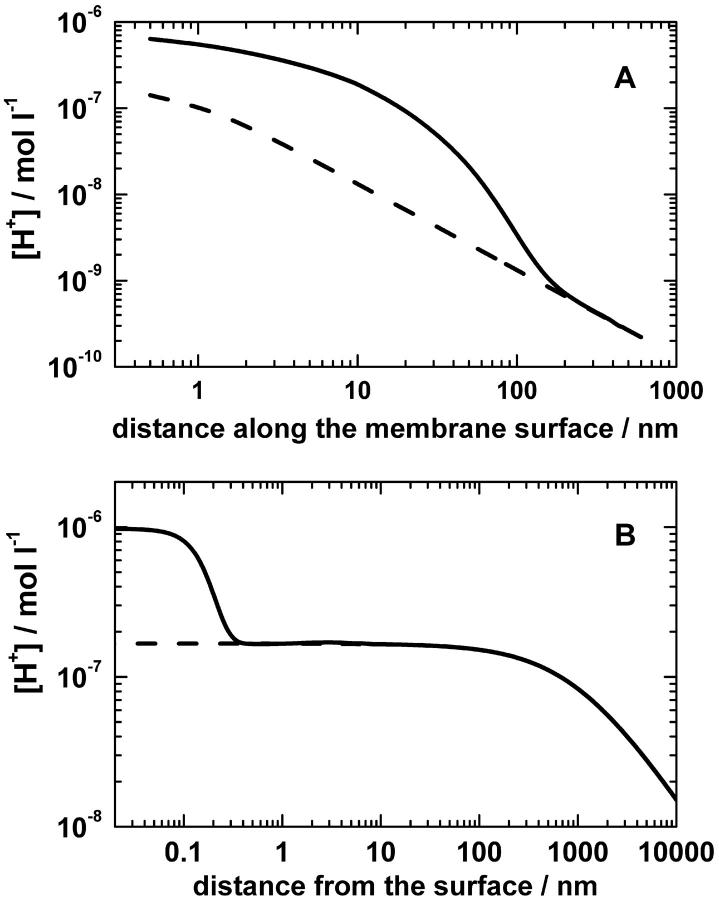
FIGURE 2.
Steady-state pH-profiles at the surface of a proton-ejecting membrane. (A) Proton distribution along a planar membrane containing only one proton pump. The cylindrical axis z is perpendicular to the membrane plane, and the axis r is directed along the membrane. The protons ejected by the pump are spread initially along the membrane surface and then escape through the interfacial barrier (no proton sinks in the membrane were considered). The turnover rate of the pump was 5 × 102 s−1, the height of the potential barrier was 0.12 eV, the surface potential was −0.06 V, the bulk diffusion coefficient of protons was 10−4 cm2/s, and the other details of the model are described in the text. (B) Steady-state pH profile at the surface of sealed membrane vesicles with the radius of 1 μm and the surface pump density of 2 × 1011 cm−2. The potential barrier as calculated for the ionic strength of 0.1 M in Fig. 1 B (solid line) was used on modeling. The dashed line shows the proton concentration as calculated without potential barrier.