TABLE 1B.
Computed 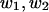 with 48 points on the boundary, at the same selected points
with 48 points on the boundary, at the same selected points  as in Table 1 A, computed
as in Table 1 A, computed 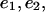 to be compared with the exact values,
to be compared with the exact values,  are the rate of convergence when compared to the coarser grid
are the rate of convergence when compared to the coarser grid
| Node | w1 | w2 | e1 | e2 | r1 | r2 | q1 | q2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.000149 | −0.000091 | 1.49(−4) | 0.91(−4) | 5.63 | 0.53 | 8.40 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 1.931862 | −0.518158 | 1.04(−5) | 5.20(−4) | 9.25 | 0.94 | ||
| 3 | 1.731796 | −1.001094 | 2.55(−4) | 1.09(−3) | 3.84 | 1.07 | 1.76 | 5.03 |
| 4 | 1.413760 | −1.416040 | 4.54(−4) | 1.83(−3) | 0.65 | 0.62 | ||
| 5 | 0.999445 | −1.734516 | 5.55(−4) | 2.47(−3) | 0.96 | 0.85 | 4.33 | 1.49 |
| 6 | 0.517242 | −1.934964 | 3.96(−4) | 3.11(−3) | 1.55 | 1.20 |
 are the rate of convergence when a grid of 24 points is compared to a grid with 12 points. For example, the computed error
are the rate of convergence when a grid of 24 points is compared to a grid with 12 points. For example, the computed error  in the fourth column means that
in the fourth column means that  The rates of convergence are
The rates of convergence are 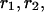 when compared to the coarser grid. The computed rate of the convergence is defined by
when compared to the coarser grid. The computed rate of the convergence is defined by 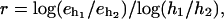 where
where  are the errors in the traction for two different grids with meshes
are the errors in the traction for two different grids with meshes  Here
Here  are the meshes that correspond to 24 and 48 points, respectively.
are the meshes that correspond to 24 and 48 points, respectively.  are the rate of convergence when a grid of 24 points is compared to a grid with 12 points.
are the rate of convergence when a grid of 24 points is compared to a grid with 12 points.
