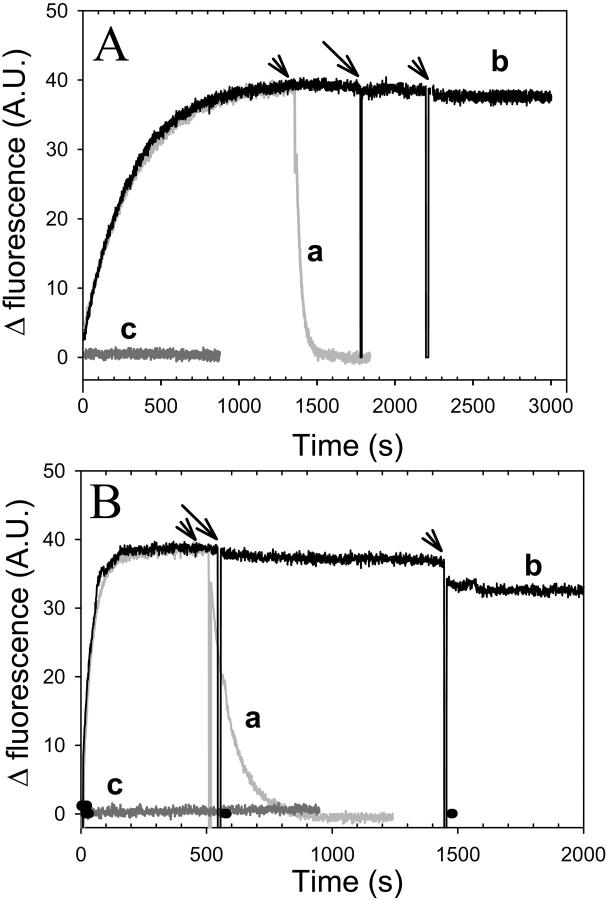
FIGURE 2.
Nucleotide exchange inhibition by gelsolin-S1. Nucleotide exchange in the gelsolin-S1 complex with Ca-ATP-actin (A) and Mg-ADP-actin (B) was monitored via changes in fluorescence intensity upon ɛ-nucleotide release from, or incorporation into, the nucleotide-binding cleft on actin. 100 μM ɛ-ATP (A) or ɛ-ADP (B) was added at the zero time to 2.0 μM actin in 10 mM HEPES buffer, at pH 7.5, containing 1 mM DTT, and either 30 μM CaCl2 and 5.0 μM ATP in A, or 30 μM MgCl2 and 5.0 μM ADP in B. Etheno-nucleotide release was initiated by the addition of 1.0 mM ATP (marked by arrowheads above curves a and b). Curve a, data in gray; no gelsolin-S1 present. Curve b, data in black; 4.0 μM gelsolin-S1 was added to this sample after the fluorescence increase due to etheno-nucleotide incorporation reached a plateau (indicated by the arrow). Curve c, data in dark gray; 4.0 μM gelsolin-S1 was added 5 min before the addition of ɛ-ATP or ɛ-ADP to G-actin (at the zero time). In all cases nucleotide exchange was abolished in the presence of gelsolin-S1.