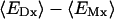TABLE 3.
Various average properties from the GpA simulations
| Helix-to-helix interaction energies, kcal/mol¶
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hmemb Å | γ, kcal/(mol · Å2) | H-bond,* % | Tilt angle,† degree | Crossing angle,‡ degree | RMSD,§ Å | 𝒲 | Uvdw | 𝒲elec | ΔGnp | |
| Dimer | ||||||||||
| D1 | 25 | 0.04 | 94 ± 5 | 25.9 ± 5.0 | −48.3 ± 3.4 | 1.18 | −56.4 ± 5.0 | −49.1 ± 3.3 | −3.0 ± 2.7 | −4.2 ± 1.1 |
| 93 ± 7 | 24.2 ± 5.0 | |||||||||
| D2 | 29 | 0.04 | 92 ± 8 | 21.8 ± 3.7 | −42.5 ± 2.5 | 1.09 | −56.9 ± 3.4 | −52.1 ± 3.1 | −2.6 ± 1.3 | −2.2 ± 0.6 |
| 90 ± 9 | 21.6 ± 3.9 | |||||||||
| D3 | 29 | 0.03 | 92 ± 7 | 22.8 ± 3.4 | −41.6 ± 2.6 | 1.09 | −56.0 ± 3.5 | −51.8 ± 3.1 | −2.6 ± 1.0 | −1.5 ± 0.4 |
| 89 ± 14 | 19.6 ± 3.3 | |||||||||
| D4 | 31 | 0.04 | 92 ± 6 | 20.7 ± 3.1 | −40.0 ± 2.5 | 0.99 | −55.0 ± 3.5 | −51.3 ± 3.2 | −2.3 ± 1.2 | −1.3 ± 0.5 |
| 89 ± 11 | 20.2 ± 3.2 | |||||||||
| Monomer | ||||||||||
| M1 | 25 | 0.04 | 59 ± 38 | 30.9 ± 4.0 | – | 2.31 | – | – | – | – |
| M2 | 29 | 0.04 | 86 ± 9 | 18.8 ± 5.5 | – | 0.92 | – | – | – | – |
| M3 | 29 | 0.03 | 90 ± 9 | 14.8 ± 6.1 | – | 0.92 | – | – | – | – |
| M4 | 31 | 0.04 | 90 ± 10 | 11.3 ± 5.0 | – | 0.96 | – | – | – | – |
The average and fluctuations of the GpA simulations were calculated from 2.6-ns trajectories (after 0.6 ns) for each run.
The average hydrogen-bond frequency was taken from residues i = 74 to i = 90. The definition of a H-bond is the same as used in Fig. 5 B. In the case of the dimer simulations, the values are given separately for each monomer.
The tilt angle is defined by the angle between the membrane interface and the principal axis of the backbone heavy atoms of Leu75 to Ile91. In the case of the dimer simulations, the values are given separately for each monomer.
The crossing angle is measured by the angle between two principal axes defined by the backbone heavy atoms of each monomer from Leu75 to Ile91. The negative sign means that it forms a right-handed dimer.
The root mean-square deviation (RMSD) of the backbone atoms of the transmembrane domain (Leu75–Ile91) relative to one of the solution NMR structures (PDB code: 1AFO).