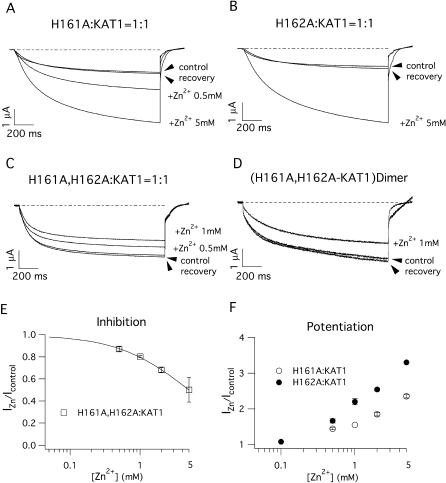
FIGURE 6.
Sensitivity to external Zn2+ of heteromeric channels comprising KDC1 mutated in the S3–S4 histidines. Typical ionic currents recorded in oocytes coinjected with (A) H161A and KAT1 and (B) H162A and KAT1. In both cases, the addition of Zn2+ resulted in an increase in the ionic current. (C) On the contrary, the current evoked by the KDC1 double mutant H161A,H162A coinjected with KAT1 is slightly blocked by the addition of Zn2+. (D) Inhibition of the current induced by Zn2+ on the heterodimeric double mutant H161A,H162A-KAT1. (E) Magnitude of the inhibition and (F) potentiation as a function of Zn2+ concentration. Steady-state current in the presence of Zn2+ (IZn) was normalized with respect to the control (Icontrol). In E the continuous line represents the best fit of the Hill equation with Ki = 4.98 mM and n = 0.8. Data represent mean ± SE from at least three experiments. Other conditions as in Fig. 5. Standard ionic solution, pH 5.6.