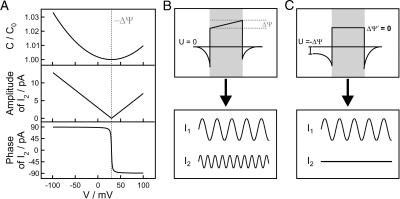
FIGURE 3.
Voltage-dependence of the capacitance, amplitude, and phase of the second harmonic (A). For inner field compensation measurements, an ac excitation is applied to planar lipid membranes resulting in a current response in the first and the second harmonic (I1 ≠ 0, I2 ≠ 0) (B). When applying an external transmembrane voltage U = −ΔΨ, the second harmonic vanishes (I1 ≠ 0, I2 = 0) (C) and the inner membrane potential difference ΔΨ′ resulting from the inner membrane and the transmembrane potential profile is zero.