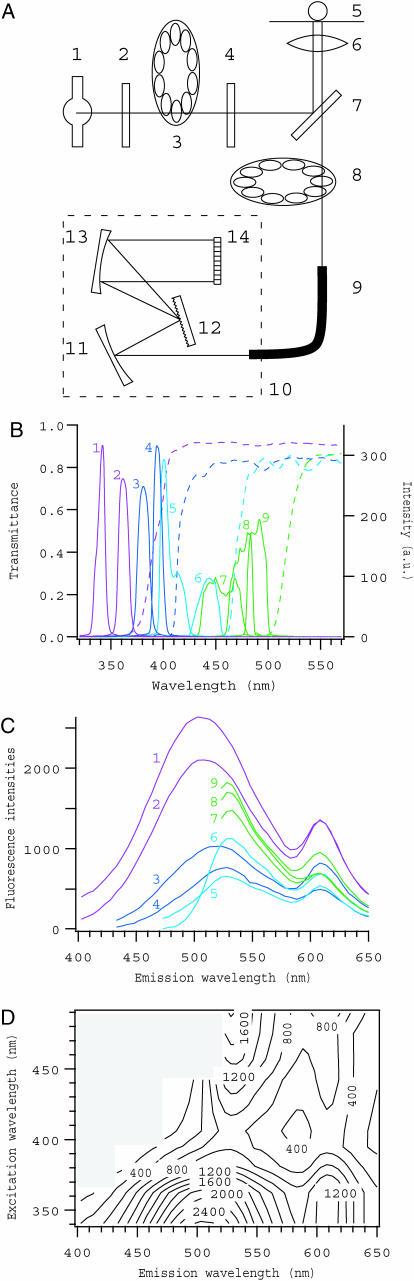
FIGURE 1.
Overview of the system for fluorescence microspectroscopy. (A) Schematic drawing of the optical setup. 1, xenon lamp; 2, heat-absorption filter; 3, excitation filter wheel; 4, neutral density filter; 5, specimen; 6, objective lens; 7, dichroic mirror; 8, barrier filter wheel; 9, quartz optical fiber; 10, spectrometer; 11–13, Czerny-Turner mount of grating and mirrors; 14, cooled CCD sensor. (B) Spectra of excitation light obtained through various interference filters with a common dichroic mirror (solid lines, numbered as 1–9), and transmittances of longpass barrier filters (dashed lines). Matching colors indicate the combinations of excitation filters with barrier filters. (C and D) An example of emission spectra at nine excitation wavelengths, and its contour presentation. It was obtained by measuring fluorescence from a 0.5-μl drop of mixture of seven calcium indicators supplemented with Texas Red dextran (see text for details). The range of emission wavelength where transmittance was lower than 50% (indicated by shaded area in D) was excluded from data for further analysis.