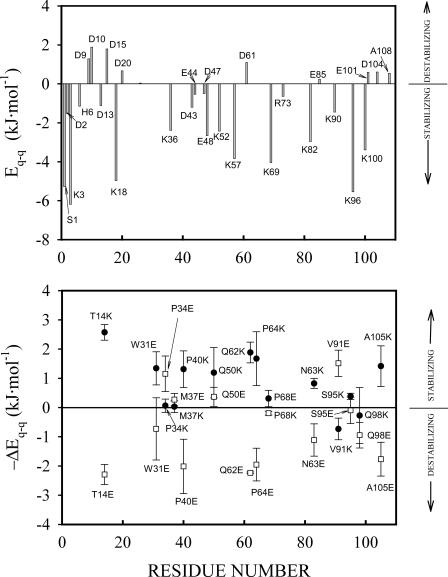
FIGURE 1.
(Upper panel) Bar graph of energies due to charge-charge interactions of all ionizable residues in the thioredoxin molecule at pH 7 as calculated using our implementation of the Tanford-Kirkwood model (see Materials and Methods for details). Positive values of Eq-q indicate that the amino acid side chains are involved in predominantly destabilizing charge-charge interactions, whereas negative values of Eq-q correspond to the amino acid side chains that are involved in predominantly stabilizing interactions. (Lower panel) Charge-charge interaction energies calculated for variants of thioredoxin in which Lys or Glu have been substituted for surface neutral polar residues. ΔEq-q is the difference between the total charge-charge interaction energy in the native state calculated for the variant and that corresponding to the WT form. The values actually plotted are −ΔEq-q, that is, the calculated contributions from charge-charge interactions in the native state to the mutation effect on denaturation ΔG. The calculations were performed for all sterically allowed rotamers of the newly introduced side chains; the average values and the corresponding standard deviations are shown.