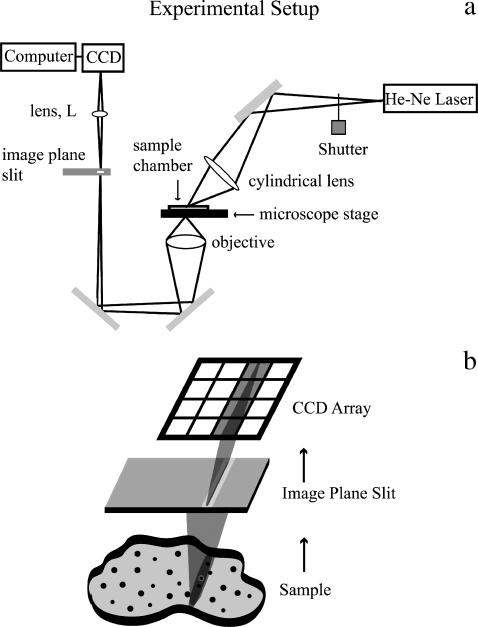
FIGURE 1.
Schematic drawing of experimental setup. (a) A cylindrical lens focuses the beam from a He-Ne laser to create a thin stripe of illumination (oriented in the page plane here) on the sample. A motorized stage controls the motion of the sample and the sample is moved in the x direction only (normal to the page plane). A 32×, 0.4 NA objective gathers the scattered light from the sample and focuses it onto a 5-μm-wide slit placed in the image plane and oriented in the direction of the illumination stripe. A lens (L) reimages the slit onto the face of a CCD camera without additional magnification. The resolution limit of the slit image cast upon the CCD camera was calculated to be on the order of one-quarter of the width of a column of pixels. Therefore, the image of the slit is reasonably sharp. (b) Detail of the imaging on the CCD array, with lenses omitted from the drawing. The slit excludes out-of-focus light and creates a well-defined focused line of scattered illumination that gets mapped onto a single column of the CCD camera array. The other columns of the CCD camera array are not illuminated.