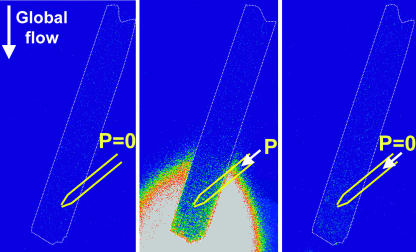
FIGURE 4.
The use of a glass pipette to locally exchange the external solution sensed by the part of the cell downstream of the pipette. The cell was positioned in the laminar bath flow (arrow indicating global flow), with the longitudinal axis almost parallel to the flow. A glass pipette, filled with solution containing 1 μM fluorescein, was positioned near the cell (marked by the white dashed line). Fluorescein was excited at 488 nm and the emitted fluorescence measured at 528 nm. No signal was detected in the absence of pressure on the glass pipette (P = 0), indicating the absence of solution flow from the pipette, i.e., the whole cell senses the bath solution (left). When applying pressure on the pipette (P), the part of the cell downstream of the pipette is exposed to the fluorescent pipette solution, as indicated by the bright fluorescein signal (middle). As soon as the pressure ceases, the solution flow from the pipette stops as well (right).