TABLE 3.
Definition of parameters and variables
| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| d | Length of one protofilament subunit (5.4 nm for actin, 8 nm for tubulin) |
| F | Force on filament end, opposing elongation |
| ΔG(+)add | Free energy change upon monomer·NTP binding to filament (+)-end |
| ΔGexchange | Free energy change upon NTP exchange with monomer-bound NDP |
| ΔGhydrolysis | Free energy change of NTP hydrolysis to form NDP and Pi |
| ΔG(−)loss | Free energy change upon monomer·NDP dissociation from filament (−)-end |
Δ
|
Free energy change upon hydrolysis of filament-bound NTP |
Δ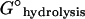
|
Standard free energy change of NTP hydrolysis to form NDP and Pi |
| ΔGPi-release | Free energy change upon reversible release of filament-bound Pi |
| k1, k−1, K1 | Forward and reverse rate constants and equilibrium dissociation constant (K1 = k−1/k1) for monomer binding to filament (+)-end (Mechanism-A) |
| k2, k−2, K2 | Forward and reverse rate constants and equilibrium dissociation constant (K2 = k−2/k2) for tracking unit translocation to terminal subunit (Mechanism-A) |
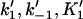 |
Forward and reverse rate constants and equilibrium dissociation constant (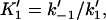 ) for monomer binding to tracking protein (Mechanism-B) ) for monomer binding to tracking protein (Mechanism-B) |
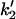 , , 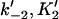
|
Forward and reverse rate constants and equilibrium dissociation constant (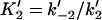 ) for monomer-tracking protein complex binding to filament end (Mechanism-B) ) for monomer-tracking protein complex binding to filament end (Mechanism-B) |
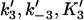 |
Forward and reverse rate constants and equilibrium dissociation constant (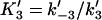 ) for tracking protein binding to terminal subunit (Mechanism-B) ) for tracking protein binding to terminal subunit (Mechanism-B) |
| kT | Thermal energy (Boltzmann constant, k, × absolute temperature, T) |
| KP | Equilibrium dissociation constant for Pi binding to filament subunits |
| Kx | Equilibrium constant for nucleotide exchange (Kx = [MT]eq[NDP] /[MD]eq[NTP]) |
| MT | NTP-bound monomer |
| MD | NDP-bound monomer |
| [MT](+)-crit | Critical concentration of NTP-bound monomers for filament (+)-ends |
| [MD](−)-crit | Critical concentration of NDP-bound monomers for filament (−)-ends |
| u | Probability of the end-tracking protein bound only to monomer (Mechanism-B) |
| α | Ratio of rate constants (k−2/k−1) in Mechanism-A |
| β | Ratio of rate constants (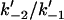 ) in Mechanism-B ) in Mechanism-B |
| γ | Ratio of rate constants (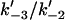 ) in Mechanism-B ) in Mechanism-B |
| ɛ | Energy captured from hydrolysis that is used for affinity modulation |
| ρ | Probability of the end-tracking protein being bound to the terminal subunit (Mechanism-A or Mechanism-B) |
