TABLE 1.
Abbreviations used in the text
| Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|
| ΔxC1–C2 | Distance from the geometric center of compartment C1 to the center of compartment C2 |
| αy and βy | Opening and closing rate constant of gate y, respectively |
| η | Position of the energy barrier controlling voltage dependence of the Na-Ca exchanger |
| γi | Activity coefficient of ion i |
| σ | [Na]o-dependence factor for fNaK |
| τy | Time constant of gate y |
| AC1–C2 | Surface area for diffusion from compartment C1 to compartment C2 |
| AP | Action potential |
| Bmax | Maximal binding capacity |
| Bmax–SR | Bmax for Ca binding within the SR |
| CICR | Ca-induced Ca release |
| [Ca]SR | Free SR Ca |
| [Ca]SRT | Total SR Ca |
| DC1–C2 | Coefficient for diffusion from compartment C1 to compartment C2 |
| d and f | Voltage-dependent activation and inactivation gates of ICa |
| Ei | Nernst potential for ion i, mV |
| ECC | Excitation-contraction coupling |
| F | Faraday constant, 96,000 Coulomb/mol |
| fCa | Ca-dependent inactivation gate of ICa |
| fCaB | Fraction of Ca-bound Ca-dependent inactivation sites of ICa |
| fNaK | Voltage-dependence parameter of INaK |
| Fxj | Fraction of total flux j in the compartment of interest |
 |
Maximal conductance of flux i |
| H | Hill coefficient SR Ca pump |
| HNa | Hill coefficient of Na-Ca exchanger for Na |
| ICa | L-type Ca current |
| INa | Fast Na current |
| INCX | Na-Ca exchange current |
| INaK | Na-K pump current |
| ISLCaP | SL Ca pump current |
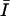 c c
|
Maximum current through channel c |
| [i]i | Free cytosolic concentration of ion i |
| [i]jct | Free junctional cleft concentration of i |
| [i]jctT | Total junctional cleft concentration of ion i |
| [i]o | Free concentration of ion i in extracellular compartment |
| [i]SL | Free concentration of ion i in the subsarcolemmal compartment |
| [i]SLT | Total concentration of i in the subsarcolemmal compartment |
| [i]T | Total cytosolic concentration of ion i |
| IPi | Portion of ICa that is carried by ion i |
| Jpump | Net SR Ca pump flux |
| JpumpF | SR Ca pump forward flux |
| JpumpR | SR Ca pump reverse flux |
| Jleak | SR Ca passive leak flux |
| JSRCaRel | SR Ca release flux |
| Ka | Ca-dependent Na-Ca exchange activation coefficient |
| kCaSR | [Ca]SR-dependent RyR activation coefficient |
| Kd | Affinity constant of ligand for ion of interest |
| Kd-SR | Kd for Ca binding within the SR |
| kim, kom, koSRCa, kiSRCa | Rate transition constants for the RyR (Fig. 4) |
| kiCa, koCa | Baseline, non-SR-dependent transition rate constants for the RyR |
| kleak | SR leak rate constant |
| Kmi | Km of Na-Ca exchanger for ion i |
| Kmf | Km SR Ca pump forward mode |
| Kmr | Km SR Ca pump reverse mode |
| kon | On rate for binding |
| koff | Off rate for binding |
| ks | SR Ca release rate constant |
| ksat | Saturation factor of the Na-Ca exchanger at very negative potentials |
| m, h, and j | Activation gate, fast inactivation gate, and slow inactivation gate, respectively, of INa |
| MaxSR, MinSR, EC50-SR, HSR | Parameters for [Ca]SR-dependent activation of SR Ca release |
| Pi1i2 | Permeability of channel to ion i1 relative to ion i2 |
| Q10-J | Temperature adjustment factor |
| R | Gas constant, 1.987 calories/mol/K |
| Rc, Xc, Yc | Gates of channel c |
| RyR | Ryanodine receptor |
| SL | Sarcolemma |
| SR | Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
| T | Absolute temperature, K |
| V | Membrane voltage |
| Vmax | Vmax SR Ca pump |
| zi | Valence of ion i |
