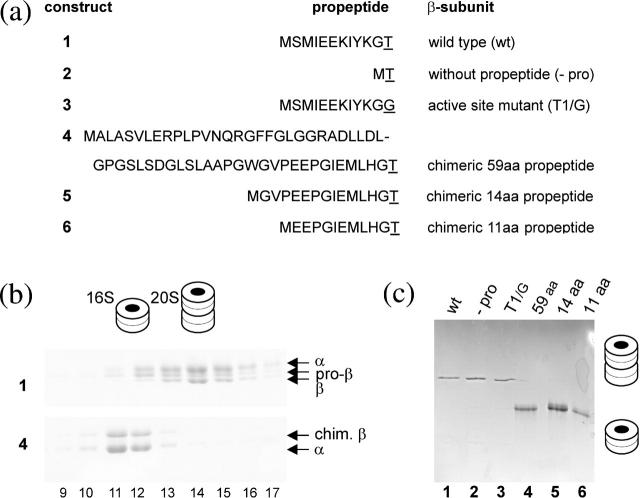
FIGURE 1.
Biochemical analysis of proteasome precursor intermediates. Gels were stained with Coomassie blue and band identity was verified by mass spectrometry. (a) Various β-subunit constructs with the nomenclature on the right and the respective propeptide sequences on the left with the active sites underlined. (b) Sucrose gradient fractionation of in vitro assembled complexes of A. fulgidus wild-type proteasome (top panel) and that with the chimeric β-subunit (bottom panel). The 16S precursor complexes are in fractions 11 and 12, whereas fractions 14–16 contain 20S complexes (proteasomes and preholoproteasomes). Band identities and two- and four-ring structures are indicated. (c) Native gel analysis of the indicated proteasome and proteasome precursor complexes of A. fulgidus wild type and their mutated derivatives resulting in 20S complexes (constructs 1–3). The chimeric proteins bear the full length (59 aa) and truncated (14 and 11 aa) human β5 propeptides (constructs 4–6) and are arrested in the 16S stage. Two- and four-ring cartoons symbolize the structure of the complex.