Figure .
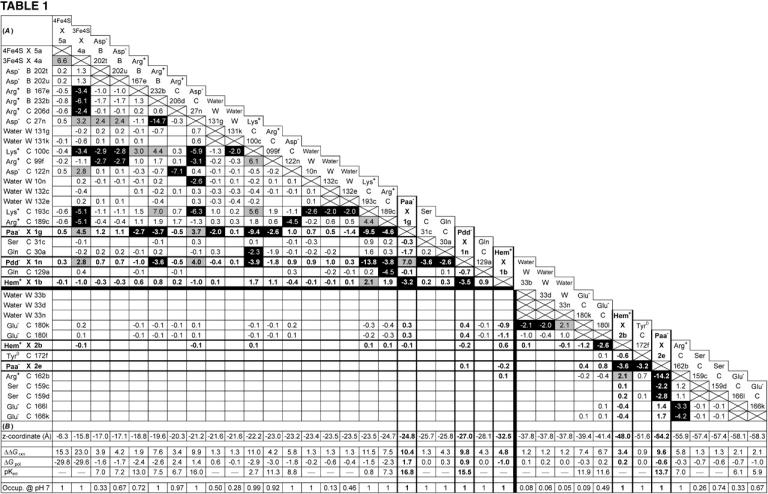
(A and B) Mutual electrostatic interaction energies in the oxidized state 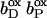 of model W. (A) All interaction energies are given in ΔpK units. Entries above ±2 ΔpK units are highlighted: positive values in shading and negative values in black. Residues are specified by the residue name, the protein chain, the residue number in the chain, and the individual conformer. Entries of value 0.0 have been omitted for clarity. The five rows and columns containing entries for hemes (Hem) and propionates (Paa− X 1, Pdd− X 1, Hem+ X 1, Hem+ X 2, and Paa− X 2) are highlighted with bold frames and bold numbers. All entries are sorted with respect to the z coordinate of the conformer. The horizontal and vertical black lines indicate the separation of strong interactions within the upper-left part and within the lower-right part of the table, respectively. (B) The z coordinate of the listed conformers in Å, starting with the [4Fe-4S] center on the cytoplasmic side and ending with Glu C166 close to the periplasmic side of the membrane (the z axis is normal to the membrane plane). The z coordinates of the following residue atoms (nomenclature as in the PDB file) are quoted: CZ (Arg), CG (Asp), CD (Glu), NZ (Lys), CD (Gln), OG (Ser), OH (Tyr), FE (Hem), CGA (Paa), CGD (Pdd), FE1 [4Fe-4S], FE1 [3Fe-4S], and OH (HOH). Additional entries are the contributions of loss of reaction field energy (ΔΔGrxn) and pH-independent polar interactions (ΔGpol) to the intrinsic pKint value of the specific conformer. The last row of this table features the conformer occupancy at pH 7.
of model W. (A) All interaction energies are given in ΔpK units. Entries above ±2 ΔpK units are highlighted: positive values in shading and negative values in black. Residues are specified by the residue name, the protein chain, the residue number in the chain, and the individual conformer. Entries of value 0.0 have been omitted for clarity. The five rows and columns containing entries for hemes (Hem) and propionates (Paa− X 1, Pdd− X 1, Hem+ X 1, Hem+ X 2, and Paa− X 2) are highlighted with bold frames and bold numbers. All entries are sorted with respect to the z coordinate of the conformer. The horizontal and vertical black lines indicate the separation of strong interactions within the upper-left part and within the lower-right part of the table, respectively. (B) The z coordinate of the listed conformers in Å, starting with the [4Fe-4S] center on the cytoplasmic side and ending with Glu C166 close to the periplasmic side of the membrane (the z axis is normal to the membrane plane). The z coordinates of the following residue atoms (nomenclature as in the PDB file) are quoted: CZ (Arg), CG (Asp), CD (Glu), NZ (Lys), CD (Gln), OG (Ser), OH (Tyr), FE (Hem), CGA (Paa), CGD (Pdd), FE1 [4Fe-4S], FE1 [3Fe-4S], and OH (HOH). Additional entries are the contributions of loss of reaction field energy (ΔΔGrxn) and pH-independent polar interactions (ΔGpol) to the intrinsic pKint value of the specific conformer. The last row of this table features the conformer occupancy at pH 7.
